Capital:
Washington DC
Area:
9,826,675 sq km (3,794,100 sq miles)
Population:
316,668,567 (2013 est)
Currency:
1 dollar = 100 cents
Religions:
Protestant 51.3%; Roman Catholic 23.9%; Jewish 1.7%; Mormon 1.7%
Ethnic Groups:
White (including Hispanic) 81.7%; Black 12.9%; Asian 4.2%; Amerindian and Alaska native 1.0%
Languages:
English; Spanish; numerous minority or immigrant languages
International Organizations:
UN; OAS; NATO; OECD; Colombo Plan; ANZUS Pact; OSCE; NAFTA; Secretariat of the Pacific Community; WTO
The world’s fourth largest country, comprising the central belt of North America together with Alaska, Hawaii, Puerto Rico, and many small Pacific Ocean islands. Mainland USA is bounded by Canada on the north, generally along latitude 49° N and the Great Lakes, and by Mexico on the south, generally at about 32° N and along the Rio Grande.
Physical
The West Coast is a series of mountain ranges with attendant valleys and plateaux running roughly parallel to the Pacific coast. In the north, the Cascade Range is cut by the valley of the Columbia River. In California, the reverse slopes of the Coast Range descend to the Sacramento and San Joaquin valleys, which are fringed inland by the snow-capped peaks of the Sierra Nevada. From here the Great Basin of Nevada and parts of Oregon, Idaho, Utah, and California extend eastward to the Rocky Mountains. The Rockies are the ‘Great Divide’, the main watershed of the country. Out of their massive ranges in Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, and New Mexico (the Mountain States), emerge the westward-running Snake and Colorado rivers, and the eastward-flowing tributaries of the Mississippi. The Great Plains, occupied by the Dakotas, Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas, are cut through by the eastward flows and have become a great prairie supporting cattle ranching and wheat cultivation. The prairies extend through the Middle West (including Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, and north-west Arkansas) to the basin of the Mississippi. In the southern states of Louisiana, Mississippi, Tennessee, Alabama, and Georgia, the main crops are cotton, rice, tobacco, and sugar cane. In this region also there are oilfields which extend into the Gulf of Mexico. The south-eastern coastal plain, occupied by Virginia, the Carolinas, and eastern Georgia, is drained by the rivers of the Appalachian Mountains and supports much mixed farming. Mountainous New England, the north-eastern region, experiences harsh winters but contains rich pastures. Inland, the Great Lakes form a great transport artery and provide hydroelectric power for the northern states.
Economy
The US economy is the world’s largest and a leader in most economic sectors. It benefits from abundant natural resources and a large internal market; mineral resources include coal, oil, and many metals. Industry, which accounts for one-fifth of GDP, is widely diversified and includes oil, steel, vehicles, aerospace, telecommunications, chemicals, electronics, food processing, consumer goods, lumber, and mining. The main agricultural crops are maize, wheat, and other grains, fruit, vegetables, and cotton. Fishing, forestry, and livestock are also substantial. The USA is the home of many multinational companies, and New York is a leading global financial centre.
History
The indigenous peoples of North America probably came from Asia across the Bering land bridge over 30,000 years ago. From the territory now occupied by Alaska, they spread out to populate the entire continent (and South America). By 1600 ad, it is estimated that there were around 1.5 million Native Americans in what are now Canada and the USA. European colonization of the eastern seaboard of North America began in the early 17th century, gaining momentum as the rival nations, most notably the British and French, struggled for control of the new territory. The Treaty of Paris (1763) marked the final triumph of Britain, but by that time the British colonies, stretching from New England in the north to Georgia in the south, had become accustomed to a considerable measure of independence. British attempts to reassert central authority produced first discontent and then open resistance. The First Continental Congress met in 1774 to consider action to regain lost rights, and the first armed encounters at Lexington and Concord in April 1775 led directly to full-scale revolt and to the formal proclamation of the separation of the Thirteen Colonies from Britain, as the United States of America, in the Declaration of Independence (4 July 1776). In the American War of Independence, which lasted until 1783, the American cause was assisted by France and Spain. The war ended with the Peace of Paris (1783), which recognized US independence.
A structure of government for the new country was set out in the Constitution of 1787, which established a federal system, dividing power between central government and the constituent states, with an executive President, a legislature made up of two houses, the Senate and the House of Representatives, and an independent judiciary headed by the Supreme Court (see also congress). Territorial expansion followed with the Louisiana Purchase of 1803, the acquisition of Florida between 1810 and 1819, and of Texas, California, and the south-west following the Mexican–American War of 1846 to 1848. The western lands of the Louisiana Purchase and those seized from Mexico were at first territories of the USA, administered by officers of the federal government. When the population reached some 60,000 an area of territory negotiated to be admitted to the Union as a new state. The mid-19th century was dominated by a political crisis over slavery and states’ rights, leading to the secession of the Southern states and their reconquest in the American Civil War of 1861 to 1865. The final decades of the century saw the westward expansion of European settlement, the purchase of Alaska (1867), and the acquisition of Spanish overseas territories after the Spanish–American War of 1898. In the 20th century the USA has participated in the two World Wars and has gradually emerged from isolationism to become a world power, a process accelerated by the Cold War division. After the disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991 US foreign policy concentrated on the resolution of major regional disputes and on providing military support for UN peacekeeping operations around the world. This changed with the election of George W. Bush as President in 2000 and the terrorist attacks on New York of September 11 2001. The USA launched a war on terrorism that involved a policy of confrontation with states whose regimes it considered to be sponsors of terrorism. In some cases this led to military intervention and forcible “regime change”, which was also influenced by a belief in the benefits of spreading democracy and freedom (see neoconservatism). Thus, the USA waged war on and deposed the Taliban in Afghanistan (2001) and Saddam Hussein in Iraq (2003) and established democratic regimes in their places. In 2008, the Democrat Barack Obama was elected president, the first African American to hold the office. He swiftly intervened in the US economy to help cushion the worst effects of the global economic crisis resulting from the Credit Crunch but soon faced strong opposition to his health-care reforms. In 2010 the Democrats lost control of the House of Representatives to the increasingly right-wing Republicans. With his own supporters disillusioned over what he had been able to achieve, Obama’s successful campaign for re-election in 2012 against the Republican Mitt Romney was closely fought. Although he was victorious, he was then restricted by Republican control of the House and, from 2015, of the Senate. He did restore diplomatic links with Cuba and signed a deal to contain Iran’s nuclear power programme (2015), although he was criticized for not intervening more assertively in Syria.
The 2016 presidential election was won by the Republican candidate, the populist maverick Donald Trump. His policies, which include restrictions on immigration, have been characterized as nationalist, protectionist, and non-interventionist in foreign policy. From mid-2017 his presidency was increasingly overshadowed by a Special Counsel investigation into alleged coordination between Trump’s presidential campaign and the Russian government. Trump was impeached in 2019 on charges of abuse of power and obstruction of justice but was acquitted.
Following a contentious election in November 2020, despite many recounts demanded by Trump, Joe Biden (with Kamala Harris as Vice-President) and the Democratic Party were successful, with Biden inaugurated in January 2021. Trump was impeached a second time in 2021, a week before he left office.
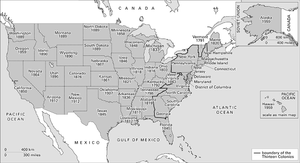
United States of America. An Ordinance of 1787 laid down that when a US territory area reached a population of 60,000 free inhabitants it could petition Congress for admission to the Union as a state. Vermont and Kentucky were early admissions and many western states followed during the 19th century.
Source: MAPS IN MINUTES™ © RH Publications (1997)
- Grotthuss–Draper law
- ground
- ground absorption
- ground anchor
- ground capacitance
- ground clutter
- Ground Communications Facilities
- ground control
- ground-control point
- ground crew
- ground current
- ground data
- ground data system
- grounded-base connection
- grounded-collector connection
- grounded-emitter connection
- grounded theory
- ground electrode
- ground failure
- ground frost
- ground ice
- ground information
- groundmass
- ground meristem
- ground moraine