The logical connective combining two statements, truth values, or formulas P and Q in such a way that the outcome is true if either P or Q or if both P and Q is true (see table). The latter outcome distinguishes the OR from the exclusive-OR operation. The OR operation is usually denoted by ∨ and occasionally by +. It is one of the dyadic operations of Boolean algebra and is both commutative and associative.
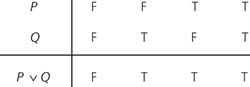
OR operation. Truth table
One way of implementing the OR operation (e.g. in Lisp) is to test P first, and then evaluate Q only if P is false. The resulting operation is noncommutative; in some languages there is a distinct notation for this.
When it is implemented as a basic machine code instruction, OR usually operates on pairs of bytes or pairs of words. In these cases the OR operation defined above is normally applied to pairs of corresponding bits.
- equatorial trough
- Equatorial undercurrent
- equiangular(of figures)
- equiangular spiral
- equiangular(within a figure)
- equiareal
- equicontinuity
- Equidae
- equidistant
- equifinality
- equilateral
- equilibrium
- equilibrium constant
- equilibrium distillation
- equilibrium flow
- equilibrium law
- equilibrium line
- equilibrium moisture
- equilibrium price
- equilibrium process
- equilibrium quantity
- equilibrium ratio
- equilibrium species
- equimolar counter-diffusion
- equinoctial colure