A special form of computer processor. The fundamental bit-slice device is a microprocessor slice, which is the execution unit for a simple CPU with a small data word size, typically 4 bits. The key property of a k-bit processor slice is the fact that n copies of the slice can be interconnected in a simple and regular manner to form an nk-bit processor that performs the same functions as a single slice on nk-bit rather than k-bit operands. The processor slices are interconnected in the form of a cascade circuit, or one-dimensional array (see diagram).
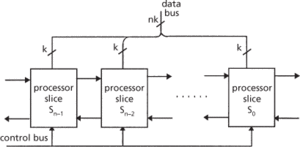
General structure of an nk-bit bit-slice microprocessor
The term ‘bit slicing’ arises from the similarity between the processor array and a large processor that has been sliced into n identical subprocessors, each operating on a k-bit portion or slice of the data being processed by the array. As indicated in the diagram, the same control lines are connected to all slices so that, in general, they all perform the same operations at the same time; these operations are independent of n, the number of slices in the processor array. The k-bit data buses that transmit operands to or from the slices are simply merged to form kn-bit data buses for the array.
- unitary taxation
- unitary transformation
- unit cell
- unit circle
- unit cube
- unit delta function
- unit distance
- United Arab Emirates
- United Arab Republic
- United Democratic Front
- United Empire Loyalists
- United Federation of Labour
- United Irishmen
- United Kingdom
- United Kingdom Industrial Space Committee
- United Kingdom Infrared Telescope
- United Kingdom Schmidt Telescope
- United Kingdom Space Agency
- United Kingdom – Disaster Monitoring Constellation-2
- United Launch Alliance
- United Malays National Organization
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
- United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child
- United Nations Development Programme
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization