A test suitable for testing the null hypothesis of independence between two dichotomous variables (see categorical variable) using data from a population subdivided into L classes: it is, therefore, a test for use with a 2×2×L contingency table. The test, which was introduced in 1959 by Mantel and Haenszel, is most used in medical contexts where, for example, one variable is outcome (‘success’ or ‘failure’), one variable is treatment (‘control’ or ‘new’), and the L classes correspond to different patient categories. The test assumes that any association between the dichotomous variables is unaffected by the third variable.
The test statistic, M, is computed as follows. Denote by fjkl the number of patients in class l (=1, 2,…, L) who experience outcome j (=1 or 2) when given treatment k (=1 or 2). Write f0kl=f1kl+f2kl, fj0l=fj1l+fj2l, and f00l=f10l+f20l. Then
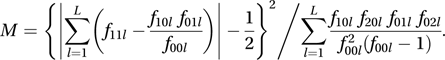 Under the null hypothesis, the distribution of M is approximated by a chi-squared distribution with one degree of freedom. When L=1 the test is equivalent to the Yates-corrected chi-squared test (see two-by-two table). The ½ term is a continuity correction.
Under the null hypothesis, the distribution of M is approximated by a chi-squared distribution with one degree of freedom. When L=1 the test is equivalent to the Yates-corrected chi-squared test (see two-by-two table). The ½ term is a continuity correction.The test combines information from each of the L classes. In a similar way, the Mantel–Haenszel statistic, ψ, combines information about the strength of the relationship between the dichotomous variables. This statistic, given by
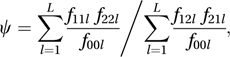 is an aggregate estimate of the odds ratio (see two-by-two table) for the two variables.
is an aggregate estimate of the odds ratio (see two-by-two table) for the two variables.
- epilimnion
- Epimenides
- epimerism
- Epimetheus
- epimorphism
- epinephrine
- epipelagic zone
- epiphany
- epiphenomenalism
- epiphenomenon
- epiphysis
- epiphyte
- Epiphyton
- EPIRB
- episodic evolution
- episome
- epistasis
- epistemic logic
- epistemic privacy
- epistemic relativism
- epistemics
- epistemology
- epitaxial transistor
- epitaxy
- epitheca