A substance that is released at some (cholinergic) nerve endings. Its function is to pass on a nerve impulse to the next nerve (i.e. at a synapse) or to initiate muscular contraction. Once acetylcholine has been released, it has only a transitory effect because it is rapidly broken down by the enzyme cholinesterase.
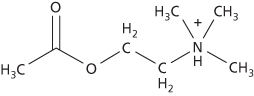
Acetylcholine
One of the main neurotransmitters of the vertebrate nervous system. It is released at certain (cholinergic) nerve endings and may be excitatory or inhibitory; it initiates muscular contraction at neuromuscular junctions and controls many physiological functions via the parasympathetic nervous system. Acetylcholine promotes contraction of smooth muscle in the gut, whereas it has an inhibitory effect on cardiac muscle, reducing heart rate. It also has a role in various brain activities, including attentiveness, aggression, sex drive, and thirst. Acetylcholine receptors (cholinoceptors) fall into two main classes, muscarinic and nicotinic receptors; hence acetylcholine can have different effects in different tissues, depending on the type of receptor. Once acetylcholine has been released it has only a transitory effect because it is rapidly broken down by the enzyme cholinesterase.
- mathematics
- mathematics education
- mathematics, philosophy of
- Mather, Cotton (1663–1728)
- Mather, Increase (1639–1723)
- Mather, Kenneth
- Matheron, Georges Francois Paul Marie (1930–2000)
- Mathiessen’s rule
- Mathilde
- MathML
- Matilda
- mating
- mating season
- mating type
- MATLAB
- matrices
- matric potential
- matrix
- matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight
- matrix game
- matrix groups
- matrix inversion
- matrix mechanics
- matrix multiplication
- matrix norm