The point in the orbits of two large bodies, A and B, where a small object subject only to Newton’s law of gravitation from A and B is stable. There are five Lagrangian points, with these points being denoted L1 to L5. Three of the points are on the line between A and B, and the other two form equilateral triangles with A and B. The complete set of Lagrangian points was discovered by Joseph-Louis Lagrange in 1772, building on earlier work by Leonhard Euler. Lagrangian points are stable positions for both natural and artificial satellites.
One of five points at which small bodies can remain in the orbital plane of two massive bodies; also known as libration points. Three of the points lie on the line joining the two massive bodies: L1 lies between them, while L2 and L3 have the two bodies between them. These three points are unstable, slight displacements of a body from them resulting in its rapid departure. The fourth and fifth points (L4 and L5) each form an equilateral triangle with the two massive bodies, 60° ahead of and behind the smaller body in its orbit around the larger one. A well-known example of bodies lying at the L4 and L5 Lagrangian points are the Trojan asteroids in Jupiter’s orbit. Among Saturn’s satellites, Telesto and Calypso lie at the L4 and L5 Lagrangian points in the orbit of the much larger Tethys. In similar fashion, tiny Helene precedes Saturn’s satellite Dione, keeping 60° ahead of Dione. The Lagrangian points are named after the French mathematician J. L. de Lagrange, who first calculated their existence. See also equipotential surface.
Lagrangian point:
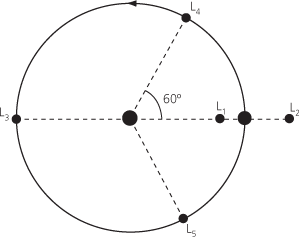
The Lagrangian points are five equilibrium points in the orbit of one body around another, such as a planet around the Sun.
One of five locations in space between two bodies where the centrifugal and gravitational forces of the two bodies neutralize each other; a third, less massive body located at any one of these points will be held in equilibrium with respect to the other two. Three of the points, L1–L3, lie on a line joining the two large bodies. The other two points, L4 and L5, which are the most stable, lie on either side of this line. For example, there is a Lagrangian point between the Earth and the Sun 1.5 million km from the Earth. Here the Sun's gravity and the Earth's gravity are equal, meaning that a spacecraft can orbit the point as if it were a planet. The points were discovered by the eighteenth-century Italian-born French mathematician Joseph Lagrange.
- Match Girls’ strike (1888)
- matching
- matching coefficient
- matching pennies
- matching problem
- bonded silvered mica capacitor
- bond energy
- bond enthalpy
- Bond, George Phillips
- Bond, George Phillips (1825–65)
- Bondi, Hermann
- Bondi, Hermann (1919–2005)
- bonding orbital
- bonding pads
- Bondi, Sir Hermann
- Bondi, Sir Hermann (1919–2005)
- Bond number
- bond order
- Bond oscillation
- bond-rating agency
- Bond, William Cranch
- Bond, William Cranch (1789–1859)
- Bond’s Work Index
- bone
- bone black