A general method for the simulation of observations of a continuous random variable X.
Let u be a pseudo-random number in the interval (0, 1) and let F be the distribution function of X. Then x, given by
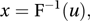 is a random observation of X. For example, an exponential random variable X, with mean μ, has distribution function (1−e−x/μ); hence −μln(1−u) is an observation of X.
is a random observation of X. For example, an exponential random variable X, with mean μ, has distribution function (1−e−x/μ); hence −μln(1−u) is an observation of X.
- pyrosulphuric acid
- pyrotechnic device
- pyroxene
- pyroxene gneiss
- pyroxene hornfels facies
- pyroxenes
- pyroxenite
- pyroxenoid
- Pyrrho of Elis (c.365–275)
- pyrrhotite
- Pyrrhus (318–272 bc)
- pyrrole
- pyrrolidine
- pyruvic acid
- Pythagoras
- Pythagoras (500 bc)
- Pythagoras (b. c.570)
- Pythagoras’ Theorem
- Pythagoras’ theorem
- Pythagorean triple
- Python
- python
- Pyxis
- PYY
- p-zone