The HVI is a composite of three variables: the percentage by which food availability falls short of 2300 kcals per capita per day in a country; the percentage of the national population that earns less than US $2 per day (measured in 2005 purchasing power parity [PPP] dollars or ‘international dollars’); and the percentage of children below the age of five in a country who are of short stature or suffering from growth failure. These three components reflect food availability within a country, average ability to access food, and a nutritional outcome. The variables are also meant to capture dimensions of vulnerability at three different scales: national (in terms of food supply), household (in terms of income), and individual (in terms of nutritional outcome). The three elements (all percentages below a threshold deemed acceptable) are then averaged to form an HVI score.
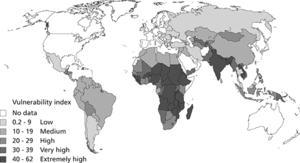
Hunger Vulnerability Index
- doublure
- doubly linked list
- doubly stochastic point process
- physics
- physics, philosophy of
- physiognomy((in ecology))
- physiological drought
- physiological saline
- physiological specialization
- physiology
- physiome
- physis
- physisorption
- phyto-
- phytoaccumulation
- phytoalexin
- phytochelatin
- phytochrome
- phytoecdysteroid
- phytogeography
- phytohaemagglutinin
- phytohormone
- phytomer
- phytoncide
- phytophagous