A test that the population being sampled has a specified distribution. It was introduced by Shapiro and Wilk in 1965. The test compares the ordered sample values with the corresponding order statistics from the specified distribution. The test is most commonly used to test for a normal distribution, in which case the test statistic, W, is given by
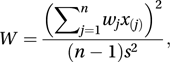 where x(j) is the jth largest of n observations, s2 is the unbiased estimate of the population variance, and wj is a function of the means, variances, and covariances of the order statistics. The Shapiro–Francia test uses a simpler substitute for wj.
where x(j) is the jth largest of n observations, s2 is the unbiased estimate of the population variance, and wj is a function of the means, variances, and covariances of the order statistics. The Shapiro–Francia test uses a simpler substitute for wj.In the case where the hypothesized distribution is exponential the statistic takes the simple form
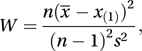 where x̄ is the sample mean. In this case, W is closely related to the inverse of the Darling test statistic, K, given by
where x̄ is the sample mean. In this case, W is closely related to the inverse of the Darling test statistic, K, given by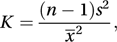 which, for n > 500, has an approximate normal distribution with mean and variance .
which, for n > 500, has an approximate normal distribution with mean and variance .http://garfield.library.upenn.edu/classics1985/A1985AKN3000001.pdf The genesis of the test.
- Pantheismusstreit
- PANTONE
- pantothenic acid
- Pantotheria
- pantry food
- papacy
- papagayo
- papain
- Papal States
- papaya
- Papen, Franz von (1879–1969)
- paper capacitor
- paper chromatography
- paper mail
- paper shale
- paper slew
- paper tape
- paper tape I/O
- paper throw
- paper white display
- papilla
- Papineau’s Rebellion (1837–38)
- papovavirus
- pappus
- Pappus of Alexandria