In a right-angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
Thus, if the hypotenuse, the side opposite the right angle, has length c and the other two sides have lengths a and b, then a2 + b2 = c2. One elegant proof is obtained by dividing up a square of side a + b in two different ways as shown in the figure, and equating areas.
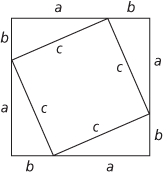
Triangles leave area c2
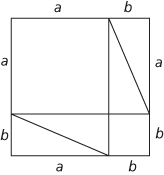
Triangles leave area a2 + b2
Pythagoras’s Theorem is a special case of the cosine rule.
- Bell, Alexander Graham
- Bell, Alexander Graham (1847–1922)
- Bellatrix
- Bell Burnell, (Susan) Jocelyn
- Bell Burnell, (Susan) Jocelyn (1943–)
- bell-curve
- bellerophontiform
- Bell, John Stuart
- Bellman, Richard Ernest (1920–1984)
- Bellman–Harris process
- Bellman’s principle of optimality
- bell metal
- Bello, Alhaji Sir Ahmadu (1906–66)
- bell pit
- bells and whistles
- bell-shaped curve
- Bell's theorem
- Bell Telephone Laboratories
- bell trend
- bellum omnium contra omnes
- Bell–Doksum tests
- Bell’s theorem
- belonging
- belonging, geographies of
- belongs to