The release of a photon from an atom or ion when an electron jumps to a lower energy level. Emission from an astronomical object indicates that there must be a source of energy within it. A hot gas radiates because the motion of the atoms causes collisions which excite electrons in the atoms to higher energy levels, or even causes them to break free of the atoms, producing ions. When the electrons return to lower energy levels, they emit the energy difference in the form of photons of specific wavelengths, giving rise to emission lines. If the electron is free (unbound) and recombines with an atom or ion, then the emission can occur at a continuous range of wavelengths, producing a continuous spectrum. See also Bound–bound Transition; Free–bound Transition.
The liberation of electrons or electromagnetic radiation from the surface of a solid or liquid, usually electrons from a metal. The outer electrons of the atoms in a metal (conduction electrons) move in a random manner among the lattice atoms with no net forces on them in the bulk of the material. Electrons near the surface of the material with directions of motion out of the surface can leave the surface, but then experience a force directing them back to the metal as the metal is left positively charged. The charge on the metal can be considered as an electric image located the same distance inside the metal as the electron is outside it. The force on the electron varies with distance x from the surface (Fig. a). As the electron moves out from the surface, work (W) is done to overcome this force (Fig. b), where
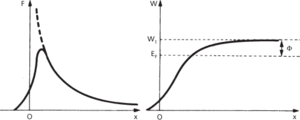
(a) Force on emitted electron as function (b) Work done to overcome force on of distance from surface emitted electron
The value W1 represents a potential barrier that must be overcome by the electron. Electrons can only escape if their energies are greater than W1. W1 is related to the work function, Φ, by
where EF is the Fermi energy.
Normally only a few electrons will have velocities, due to their thermal energy, large enough to escape (Fig. c). Emission occurs when sufficient energy is given to the electrons to allow them to escape (as in photoemission, thermionic, or secondary emission) or the potential barrier is distorted by the presence of an intense electric field (as in field emission).
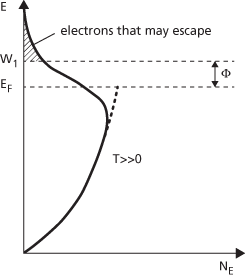
(c) Number of electrons as a function of electron energy
- nerve growth factor
- nerve impulse
- nerve net
- nervous system
- Neso
- nesosilicates
- Nespoli, Paolo Angelo (1957– )
- nesquehonite
- Nessler’s reagent
- nest
- nested blocks
- nested design
- nested hypothesis
- nested models
- nested multiplication
- nested sets
- nesting
- nesting store
- Nestorian
- Nestorianism
- Net
- net
- Netanyahu, Binyamin (1949–)
- net assimilation rate
- Net Book Agreement