The range of wavelengths over which electromagnetic radiation extends. The longest waves (105−10−3 metres) are radio waves, the next longest (10−3−10−6 m) are infrared waves, then comes the narrow band (4−7×10−7 m) of visible light, followed by ultraviolet waves (10−7−10−9 m), X-rays (10−9−10−11 m), and gamma rays (10−11−10−14 m). Microwaves are at the lower-wavelength end of the radio-wave division (0.03−10−3 m). See Appendix 4.
The complete range of electromagnetic radiation. From longest to shortest wavelengths, the electromagnetic spectrum consists of radio waves (105−10−3 m), infrared waves (10−3−10−6 m), visible light (4−7 × 10−7 m), ultraviolet waves (10−7−10−9 m), X-rays (10−9−10−11 m), and gamma rays (10−11−10−14 m). The speed of electromagnetic radiation, c, is constant in a vacuum (see Light, Velocity of). Since c is equal to wavelength multiplied by frequency (expressed in appropriate units), for c to remain constant the frequency must become greater as the wavelength becomes shorter. For example, radio waves have long wavelength and low frequency, but gamma rays have high frequency and short wavelength. So both wavelength and frequency can take on a wide range of values. The visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum (i.e. light), detectable by the human eye, is subdivided into red (at the long-wavelength end), orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet (the short-wavelength end).
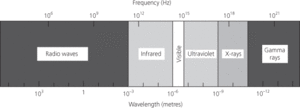
A complete range, over all wavelengths and frequencies, of electromagnetic waves. These include (in order of decreasing wavelength) radio and television waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma radiation.
The colour of sunlight is made up of a whole range of colours. A glass prism can be used to split white light into separate colours that are sensitive to the human eye, ranging from red (longer wavelength) to violet (shorter wavelength). The human eye cannot detect electromagnetic radiation outside this range. Some animals, such as bees, are able to detect ultraviolet light.
The range of wavelengths over which electromagnetic radiation extends. The longest waves (105–10−3 metres) are radio waves, the next longest (10−3–10−6 m) are infrared waves, then comes the narrow band (4–7 × 10−7 m) of visible radiation, followed by ultraviolet waves (10−7–10−9 m) and X-rays and gamma radiation (10−9–10−14 m). See Appendix 4.
The entire range of frequency of electromagnetic radiation. See Table 10, in the back matter.
The range of wavelengths over which electromagnetic radiation extends. The longest waves (105–10−3 metres) are radio waves, the next longest (10−3–10−6 m) are infrared waves, then comes the narrow band (4–7×10−7 m) of visible light, followed by ultraviolet radiation (10−7–10−9 m), X-rays (10−9–10−11 m), and gamma rays (10−11–10−14 m).
The range of frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation.
- online transaction processing
- only if
- Onnian
- on/off control
- on-off keying
- onomastics
- Onondagan
- O notation
- on-page optimization
- Onsager, Lars
- Onsager relations
- Onsala Space Observatory
- ON star
- Ontarian
- on the fly
- on-the-fly error recovery
- on-the-job training
- ontic
- onto
- onto function
- ontogenetic heterochrony
- ontogeny
- ontological argument
- ontological commitment
- ontology