The increase in a population that occurs when the birth rate is higher than the death rate, or when immigration exceeds emigration, or when a combination of these factors is present. The per capita growth rate (r) is determined by the difference between the birth rate and the death rate. Under ideal conditions the population will achieve its maximum possible value of r, called the intrinsic rate of increase (rmax). A growth curve, obtained by plotting population size against time, is typically S-shaped (sigmoid) or J-shaped (see graphs). A sigmoid growth curve shows an initial phase of exponential growth. The curve levels off when the environment has reached its carrying capacity, i.e. when food, space, and other conditions can support a given number of individuals without an increase in population numbers. A J-shaped growth curve shows an initial phase of exponential growth that ceases abruptly, with a sudden decrease in population numbers. This decrease may be caused by a number of factors, such as the end of the life cycle of the prey or any other factor contributing to environmental resistance that may suddenly take effect. See also bacterial growth curve; fecundity; reproduction rate; survivorship curve.
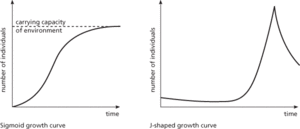
Population growth curves
The rate of increase of the world’s population has become ever faster:
year
population in billions
1850
1.2
1900
1.6
1950
2.55
2000
6.1
2050
(estimated) 9.2
‘Future population growth is highly dependent on the path that future fertility takes. In the medium variant, fertility is projected to decline from 2.6 children per woman today to slightly over 2 children per woman in 2050. If fertility were to remain about half a child above the levels projected in the medium variant, world population would reach 10.6 billion by 2050. A fertility path half a child below the medium would lead to a population of 7.6 billion by mid-century. That is, at the world level, continued population growth until 2050 is inevitable even if the decline of fertility accelerates (Population Division, Dept. Econ. & Soc. Affairs, UN Secretariat, 2004 Revision). See population projection.
Wolfgang Lutz et al. (2004) discuss expert argument-based probabilistic forecasting of population; Bongaarts and Bulatao (1999) Pop. & Devt Rev. 25 quantify the relative contributions of fertility, mortality, migration, and age structure in projections for all countries of the world.
- dish antenna
- disharmonic fold
- dish-pan experiment
- dish structure
- disilane
- disincentives
- disinfectant
- disinhibition
- disintegration
- disintegration constant
- disintermediation
- disinvestment
- disjoint
- disjoint union
- disjunct
- disjunction
- disjunction elimination
- disjunction introduction
- disjunction property
- disjunctive addition
- disjunctive kriging
- disjunctive normal form
- disjunctive syllogism
- disjunct shell
- disk