A group of water-soluble vitamins that characteristically serve as components of coenzymes. Plants and many microorganisms can manufacture B vitamins but dietary sources are essential for most animals. Heat and light tend to destroy B vitamins.
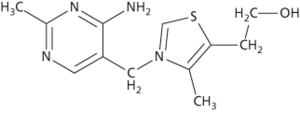
Vitamin B1 (thiamin(e)) is a precursor of the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate, which functions in carbohydrate metabolism. Deficiency leads to beriberi in humans and to polyneuritis in birds. Good sources include brewer’s yeast, wheatgerm, beans, peas, and green vegetables.
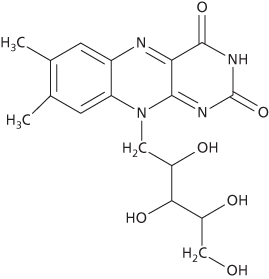
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) occurs in green vegetables, yeast, liver, and milk. It is a constituent of the coenzymes FAD and FMN, which have an important role in the metabolism of all major nutrients as well as in the oxidative phosphorylation reactions of the electron transport chain. Deficiency of B2 causes inflammation of the tongue and lips and mouth sores.
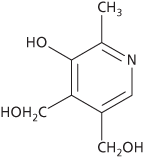
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is widely distributed in cereal grains, yeast, liver, milk, etc. It is a constituent of a coenzyme (pyridoxal phosphate) involved in amino acid metabolism. Deficiency causes retarded growth, dermatitis, convulsions, and other symptoms.
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin; cobalamin) is manufactured only by microorganisms and natural sources are entirely of animal origin. Liver is especially rich in it. One form of B12 functions as a coenzyme in a number of reactions, including the oxidation of fatty acids and the synthesis of DNA. It also works in conjunction with folic acid (another B vitamin) in the synthesis of the amino acid methionine and it is required for normal production of red blood cells. Vitamin B12 can only be absorbed from the gut in the presence of a glycoprotein called intrinsic factor; lack of this factor or deficiency of B12 results in pernicious anaemia.
Other vitamins in the B complex include nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid, biotin, and lipoic acid. See also choline.
Vitamin B1
Vitamin B2
Vitamin B6
https://www.qmul.ac.uk/sbcs/iupac/misc/B6.html Information about IUPAC nomenclature for vitamin B6 and related compounds
https://www.qmul.ac.uk/sbcs/iupac/misc/B12.html Information about IUPAC nomenclature for vitamin B12 and derivatives
A group of water-soluble vitamins that characteristically serve as components of coenzymes. Plants and many microorganisms can manufacture B vitamins but dietary sources are essential for most animals. Heat and light tend to destroy B vitamins.
Vitamin B1 (thiamin(e)) is a precursor of the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate, which functions in the Krebs cycle and carbohydrate metabolism. Deficiency leads to beriberi in humans and to polyneuritis in birds. Good sources include whole-grain or fortified cereals, beans, peas, and nuts.
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) occurs in green vegetables, yeast, liver, and milk. It is a constituent of the coenzymes FAD and FMN, which have an important role in the metabolism of all major nutrients as well as in the oxidative phosphorylation reactions of the electron transport chain. Deficiency of B2 causes inflammation of the tongue and lips, mouth sores, and conjunctivitis.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is widely distributed in cereal grains, yeast, liver, milk, etc. It is a constituent of a coenzyme (pyridoxal phosphate) involved in amino acid metabolism. Deficiency can cause anaemia, dermatitis, fatigue, and other signs.
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin or cobalamin) is manufactured only by microorganisms and natural sources are entirely of animal origin. Liver is especially rich in it. One form of B12 functions as a coenzyme in a number of reactions, including the oxidation of fatty acids and the synthesis of DNA. It also works in conjunction with folic acid (another B vitamin) in the synthesis of the amino acid methionine and it is required for normal production of red blood cells. Vitamin B12 can only be absorbed from the gut in the presence of a glycoprotein called intrinsic factor; lack of this factor or deficiency of B12 results in pernicious anaemia.
Other vitamins in the B complex include nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid, biotin, and lipoic acid. See also choline; inositol.
- Compton wavelength
- compulsion
- compulsory purchase order
- CompuServe
- computability
- computability theory
- computable
- computable algebra
- computable function
- computable functions
- computable general equilibrium model
- computable number
- computable real number
- computable set
- computable structure
- computation
- computational chemistry
- computational creativity
- computational environment
- computational fluid dynamics
- computational geometry
- computational hardness assumption
- computationally secure
- computational psychology
- Computational Statistics & Data Analysis