The stability of an atomic nucleus depends on its binding energy per nucleon, E. This energy represents the average energy that needs to be supplied to liberate a nucleon from the nucleus. One may visualize this qualitatively by imagining a well of potential energy, the depth of which represents E for a particular nucleus. Nuclei with deeper binding energy wells are more stable and occur at intermediate mass numbers. In the graph of E against mass number shown, ŋum56o26;Fe has a value of E of 8.8 MeV and is one of the most stable of nuclides. There are three other nuclides, ŋum4o2;He, ŋum12o6;C, and ŋum16o8;O lying significantly above the main curve. Though these are not the most stable of all nuclides, they are considerably more stable than those of other nuclides of adjacent mass numbers. Nuclides of intermediate masses, such as iron, have the greatest values of E. Therefore if the conditions are right, there will be a tendency for nuclides of mass lower than iron to undergo fusion to enhance stability by acquiring a deeper E well. When nuclei heavier than iron undergo fission, energy is released which is equivalent to the difference in E of the parent and daughter nuclei (see also liquid-drop model; Q-value; valley of stability).
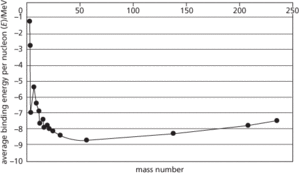
Nuclear stability.
- breadcrumb navigation
- breadcrumb trail
- bread-crust bomb
- breadth-first search
- break
- break-back thrust
- breakdown
- MDA
- MDMA
- MDM Observatory
- MDNS
- MD-plot
- MDR
- Meade, Carl Joseph (1950– )
- Meade Review
- Mead, George Herbert (1863–1931)
- Mealy circuit
- Mealy machine
- mean
- mean absolute deviation
- mean absolute error
- mean absolute percentage error
- mean anomaly
- mean chart
- mean current density