A device that consists of a number of capacitors linked by a series of switches that in practice consist of bipolar or field-effect (MOS) transistors (see diagram). These circuits can be built from discrete components but are invariably manufactured as integrated circuits. Clock pulses are applied to close the switches, a two-phase system (ϕ1 and ϕ2) being used. As each switch is closed charge is transferred from one capacitor to the next.
Bucket-brigade devices are frequently used as delay lines in both digital and analogue systems since the amount of charge stored may vary continuously from zero to the limit set by the magnitude of the capacitance and the operating voltage. The capacitors are provided in practice by using the collector-base capacitance or drain-gate capacitance of the transistors used in the circuit.
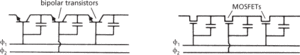
Bucket-brigade devices
- enteric nervous system
- entering variable
- enterogastric reflex
- enterokinase
- enterolithic structure
- enteron
- Enterprise
- enterprise
- enterprise culture
- enterprise decision management
- Enterprise Investment Scheme
- enterprise modelling
- enterprise resource planning
- enterprise server
- enterprise system
- enterprise wiki
- enterprise zone
- enterprise zones
- enthalpy
- enthalpy balance
- enthalpy-concentration diagram
- enthalpy (H)
- enthusiasm
- enthymeme
- entire function