Any of the hard structures in vertebrates that are used principally for biting and chewing food but also for attack, grooming, and other functions. In fish and amphibians the teeth occur all over the palate, but in higher vertebrates they are concentrated on the jaws. They evolved in cartilaginous fish as modified placoid scales, and this is reflected in their structure: a body of bony dentine with a central pulp cavity and an outer covering of enamel on the exposed surface (crown). The portion of the tooth embedded in the jawbone is the root (see illustration).
In mammals there are four different types of teeth, specialized for different functions (see canine tooth; incisor; molar; premolar). Their number varies with the species (see dental formula). See also deciduous teeth; permanent teeth.
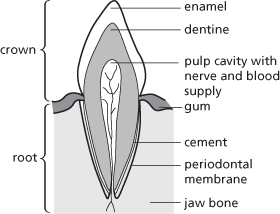
Section through an incisor tooth
- full subtractor
- full-text index
- full text retrieval
- full tree
- full-wave dipole
- full-wave rectifier
- remotely operated vehicle
- remote manipulator system
- Remote Method Invocation
- remote network monitor
- remote operations service element
- remote procedure call
- remote sensing
- remote terminal unit
- remoulding
- removable singularity
- removal time
- REM sleep
- Renaissance
- renal
- renal capsule
- renal tubule
- renaturation
- rendering
- rendezvous