A method for dividing multiple-digit natural numbers into other natural numbers. The method is ultimately the same as when dividing single-digit natural numbers but presented differently as the remainder at each stage may be multiple-digit. For example, the division of 23 into 5615 is presented above.
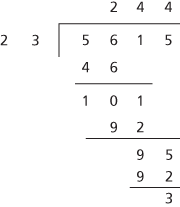
long division of integers
This shows that 5615 = 244 × 23 + 3. As with normal division of single-digit numbers, 23 does not divide into 5, but does twice into 56 with remainder 10, which is written beneath. The process continues until a remainder is found.
This notation can similarly be used for long division of polynomials. The second long division shows that
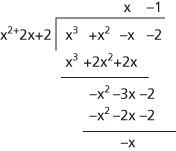
long division of polynomials
See division algorithm.
- autonomous investment
- autonomous pension funds
- autonomous spaces
- autonomous system
- autonomous system number
- autonomy/heteronomy
- autonomy of ethics
- autonymy
- autoplay
- autopolyploid
- autoprotolysis
- autoprotolysis constant
- autoradiography
- autoradiolysis
- autoregression
- autoregressive conditional heteroscedasticity
- autoregressive integrated moving average
- autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA (p, d, q)) model
- autoregressive model
- autoregressive moving average (ARMA (p, q)) model
- autoregressive process
- autoresponder
- autosave
- autosome
- autostylic jaw suspension