A pair of electrons having opposite spin in an orbital of an atom. For instance, in ammonia the nitrogen atom has five electrons, three of which are used in forming single bonds with hydrogen atoms. The other two occupy a filled atomic orbital and constitute a lone pair. The orbital containing these electrons is equivalent to a single bond (sigma orbital) in spatial orientation, accounting for the pyramidal shape of the molecule. In the water molecule, there are two lone pairs on the oxygen atom. In considering the shapes of molecules, repulsions between bonds and lone pairs can be taken into account:
lone pair-lone pair > lone pair-bond > bond-bond.
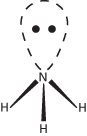
Lone pair
- charge-coupled device
- charged-body potential method
- charge density
- charge density wave
- charge hand
- charge storage
- charge-storage diode
- charge(symbol: Q; unit: coulomb)
- charge-transfer complex
- charge-transfer device
- chariot
- charioteer
- charisma
- charity, principle of
- Charlemagne
- Charles I (1600–49)
- Charles II (1630–85)
- Charles II (1661–1700)
- Charles II (823–77)
- Charles III (1716–88)
- Charles III (839–88)
- Charles I of Anjou (1226–85)
- Charles IV (1316–78)
- Charles, Jacques Alexandre César
- Charles, Jacques Alexandre César (1746–1823)