An electronic device that processes information according to a set of instructions, called the program. The most versatile type of computer is the digital computer, in which the input is in the form of characters, represented within the machine in binary notation. Central to the operation of a computer is the central processing unit (CPU), which contains circuits for manipulating the information (see logic circuits). The CPU contains the arithmetic/logic unit (ALU), which performs operations, and a control unit. It is supported by a short-term memory, in which data is stored in electronic circuits. Associated storage usually involves magnetic disks or CD-ROM. There are also various peripheral input and output devices, such as a keyboard, visual-display unit (VDU), magnetic tape unit, and printer. Computers range in size from the microprocessor with a few thousand logic elements, to the large mainframe computer with millions of logic circuits.
The analog computer is used in scientific experiments, industrial control, etc. In this type of device the input and output are continuously varying quantities, such as a voltage, rather than the discrete digits of the more commercially useful digital device. Hybrid computers combine the properties of both digital and analog devices. Input is usually in analog form, but processing is carried out digitally in a CPU.
Computer hardware consists of the actual electronic or mechanical devices used in the system; the software consists of the programs and data.
Usually a digital electronic device that carries out logical and arithmetical calculations according to a very precise set of instructions contained within a program, known as software. It typically comprises a number of different components, though in laptop and handheld computers some of these may be contained within a single unit. These components are known as computer hardware and will include input devices such as keyboard, mouse, microphone for speech recognition software, or tablet and pen; a central processing unit which carries out the actual calculations; memory storage devices such as the working memory, the computer’s hard disk drive; output devices such as a monitor and printer; and communication devices which allow computers to connect to one another or to the Internet.
A device or system that is capable of carrying out a sequence of operations in a distinctly and explicitly defined manner. The operations are frequently numerical computations or data manipulations but also include input/output; the operations within the sequence may depend on particular data values. The definition of the sequence is called the program. A computer can have either a stored program or wired program. A stored program may exist in an alterable (read/write or RAM) memory or in a nonalterable (ROM) memory. Today, the term ‘computer’ without qualification is a synonym for ‘stored-program digital computer.’ See also analogue computer, digital computer, von Neumann machine.
Any automatic device for the processing of information received in a prescribed and acceptable form according to a set of instructions. The instructions and information are stored in memory. The most widely used and most versatile of these devices is the digital computer, which can manipulate large amounts of information at high speed. Its input must be discrete rather than continuous and may consist of combinations of numbers, characters, and special symbols. Instructions – the program – are written in an appropriate programming language. The information is represented internally in binary form.
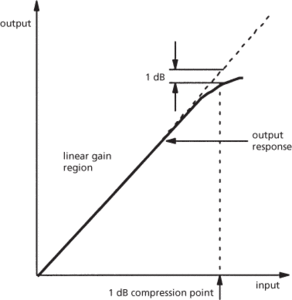
Amplifier output signal versus input signal, showing the 1 dB compression point
The development of microelectronics has allowed the corresponding development of a wide range of computers varying in size and complexity according to the required applications. Modern computers range from the microcomputer that contains typically a few billion logic circuits and a few billion words of memory to very large mainframe computers typically containing trillions of logic circuits and words of memory. The most powerful such devices are capable of performing over ten thousand trillion operations per second and can serve many users at the same time. Constant improvements in packing densities and subsequent miniaturization of circuits, coupled with improvements in speed of operation of the logic circuits is resulting in ever more powerful microcomputers and dramatic reductions in the physical size of mainframe computers.
Most computer systems consist of three basic elements: the central processing unit (CPU), the main memory, and peripheral devices involved with input/output and permanent storage of information. The CPU controls the operation of the system and performs arithmetic and logic operations on the data. The main memory stores the program and the data in units of bytes or words, each of which has a unique address, so that they may be retrieved quickly by the CPU. A cache memory is employed by high-performance systems: it interacts directly with the CPU and transfers information at extremely high speed. The information currently in active use is held in the cache. A complete computer system consists of the hardware – the electronic and other devices – and complementary software – the set of programs and data. A recent development that affects all computers from the smartphone upwards is that the CPU typically contains multiple processor cores, with internal memory, data buses, and caching.
The analogue computer is a device that accepts data as a continuously varying quantity rather than as a set of discrete items required by the digital computer. It is used in scientific experiments, simulation processes, and in the control of industrial processes where a constantly varying quantity can be monitored. A problem is solved by physical analogy, usually electrical. The magnitudes of the variables in an equation are represented by voltages fed to circuit elements connected in such a way that the input voltages interact according to the same equation as the original variables. The output voltage is then proportional to the numerical solution of the problem. It can solve or analyse many types of differential equations.
Any device capable of carrying out a sequence of operations in a defined manner. The definition of the operations is called the program. An analog computer performs computations by manipulating continuous physical variables, such as voltage and time. A digital computer operates on discrete quantities, most often represented as ‘on-off’, indicating whether the value of a binary variable is 0 or 1. Numbers and information are then represented by the binary system. Philosophically the excitement generated by computers has been in exploring the extent to which mental operations are well-represented as computations. See also artificial intelligence, Chinese room, connectionism, Turing machine, von Neumann machine.
- system security
- systems engineering
- systems house
- Systems I, II, and III
- systems integration
- systems integrator
- system software
- system specification
- systems programmer
- systems programming
- systems software
- systems theory
- systems tract
- system tables
- system temperature
- system testing
- System V
- systole
- systolic array
- Système International d’Unités
- Système Probatoire d’Observation de la Terre
- syzygy
- SZ
- Szemerédi’s theorem
- Szent-Györgyi, Albert von