A stronger form of the Chebyshev inequality. Let X1, X2,…, Xn be independent random variables with finite expected values and variances. Define the partial sum Sk by
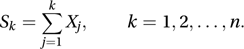 The inequality states that, for all positive values of ɛ,
The inequality states that, for all positive values of ɛ,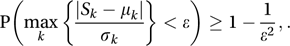 where, for each k, μk and σk2 are, respectively, the expected value and variance of Sk. See also Bernstein inequality; Hölder inequality; Markov inequality; Minkowski inequality.
where, for each k, μk and σk2 are, respectively, the expected value and variance of Sk. See also Bernstein inequality; Hölder inequality; Markov inequality; Minkowski inequality.
- geosynchronous orbit
- Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle
- geosynchronous transfer orbit
- geosyncline
- geotagging
- GEOTAIL
- Geotail
- geotail
- geotargeting
- geotaxis
- geotechnical map
- geotherm
- geothermal brine
- geothermal energy
- geothermal field
- geothermal flux
- geothermal gradient
- geothermic survey
- geothermometer
- geotropism
- geovisualization
- geo-web
- gerade
- geraniol
- geranium