Unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain one or more double carbon-carbon bonds in their molecules. In systematic chemical nomenclature alkene names end in the suffix -ene. Alkenes that have only one double bond form a homologous series (the alkene series) starting ethene (ethylene), CH2=CH2, propene, CH3CH=CH2, etc. The general formula is CnH2n. Higher members of the series show isomerism depending on position of the double bond; for example, butene (C4H8) has two isomers, which are (1) but-1-ene (C2H5CH=CH2) and (2) but-2-ene (CH3CH=CHCH3): see formulae. Alkenes can be made by dehydration of alcohols (passing the vapour over hot pumice):
An alternative method is the removal of a hydrogen atom and halogen atom from a haloalkane by potassium hydroxide in hot alcoholic solution:
Alkenes typically undergo addition reactions to the double bond. They can be tested for by the Baeyer test. See also hydrogenation; oxo process; ozonolysis; Ziegler process.
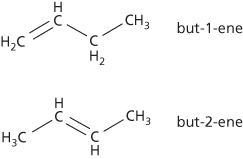
Alkenes
https://www.acdlabs.com/iupac/nomenclature/79/r79_53.htm Information about IUPAC nomenclature
- Legendre’s conjecture
- Legendre’s differential equation
- legged robots
- Leggett–Garg inequality
- Leggett’s theorem
- legion
- legume
- Leguía, Augusto Bernardino (1863–1932)
- Lehmann, Erich Leo (1917–2009)
- Lehmann, Inge
- Lehmann, Inge (1888–1993)
- Lehmann, Johann Gottlob (1719–67)
- Lehmann–Scheffé theorem
- Lehn, Jean Marie Pierre
- Leibler, Richard Arthur (1914–2003)
- Leibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm
- Leibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm (1646–1716)
- Leibniz’ law
- Leibniz’s integral rule
- Leibniz’s law
- Leibniz’s Theorem
- Leicester, Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of
- Leidenfrost effect
- Leif Ericsson
- Leighton–Pendexter classification