Methods for grouping multivariate data into clusters (see cluster analysis). Suppose there are n data items. The agglomerative clustering methods start by regarding these as n separate clusters of size 1. The two clusters judged closest together (on some criterion) are then merged to reduce the number of clusters to (n−1). This procedure could be continued until all the items would be collected into a single cluster.
The three simplest criteria are as follows. In single linkage clustering the distance between two clusters is defined as the least distance between an item in one cluster and an item in the other cluster. In complete linkage clustering, by contrast, the distance between two clusters is defined as the greatest distance between an item in one cluster and an item in the other cluster. As a compromise, group-average clustering uses the average of the distances between every member of one cluster and every member of the other cluster. The process of agglomeration is often represented using a dendrogram. See also distance measure; Ward's method.
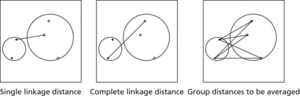
Agglomerative clustering methods. Examples of the distance definitions used in clustering.
- non-basic variables
- non-being
- nonbenzenoid aromatics
- nonbinary logic
- non-central chi-squared distribution
- non-central F-distribution
- non-centrality parameter
- non-central t-distribution
- non-classical logic
- noncoding DNA
- noncoding RNA
- non-cognitivism
- noncoherent detection
- non-combustibility
- noncommutative geometry
- non-competitive inhibition
- noncompetitive inhibition
- Nonconformist
- non-conformity
- nonconformity
- non-constructive
- non-constructive methods
- non-contact sensing
- non-contradiction, principle of
- non-contributory pension scheme