A method for generating values of a continuous random variable for use in a simulation. Suppose that the random variable X, which takes values in the interval (a, b), has probability density function f. Denote the maximum value of f(x) by M. Let u and ν be two random numbers uniformly distributed in the interval (0, 1). Write r=a+(b−a)u and s=Mν, so that r and s are uniformly distributed on (a, b) and (0, M), respectively. Calculate f(r). If f(r)>s then r is accepted as a value of X. Otherwise, it is rejected and a new pair of values is taken for u and ν.
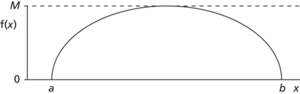
Acceptance–rejection algorithm. Uniform random numbers are generated in the intervals (a, b) and (0, M). If the point generated lies between the graph of f(x) and the x-axis, then the value of X is accepted.
http://playingwithr.blogspot.co.uk/2011/06/ R code and demonstration.
- X-ray bright point
- X-ray burst
- X-ray calorimeter
- X-ray crystallography
- X-ray diffraction
- X-ray diffraction crystallography
- X-ray fluorescence
- X-ray fluorescence spectrometry
- X-ray lithography
- X-ray nova
- X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
- X-ray photography
- X-ray powder photograph
- X-ray pulsar
- X-rays
- X-ray source
- X-ray sources
- X-ray spectrometer
- X-ray spectroscopy
- X-ray spectrum
- X-ray spectrum (DRAFT)
- X-ray telescope
- X-ray Timing Explorer
- X-ray topography
- X-ray transient