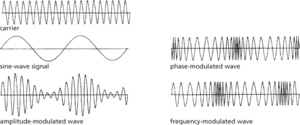
The process of changing an electrical signal. In radio transmission, it is the process of superimposing the characteristics of a periodic signal onto a carrier wave so that the information contained in the signal can be transmitted by the wave. The simplest form of modulation is amplitude modulation (AM), in which the amplitude of the carrier is increased or diminished as the signal amplitude increases and diminishes. The modulated wave is composed of the carrier wave plus upper and lower sidebands. In single-sideband modulation (SSB) the carrier and one of the sidebands of an amplitude-modulated waveform are suppressed. This saves on bandwidth occupancy and signal power. In frequency modulation (FM), the frequency of the carrier is increased or diminished as the signal amplitude increases and diminishes but the carrier amplitude remains constant. In phase modulation, the relative phase of the carrier is varied in accordance with the signal amplitude. Both frequency modulation and phase modulation are forms of angle modulation.
In pulse modulation the information is transmitted by controlling the amplitude, duration, position, or presence of a series of pulses. Morse code is a simple form of a pulse modulation.
Modulation.
The process of varying one signal, called the carrier, according to the pattern provided by another signal. The carrier is usually an analogue signal selected to match the characteristics of a particular transmission system. Modulation signals and techniques may be combined to produce composite signals carrying many independent channels of information (see multiplexing).
The primary types of modulation are as follows:
(a) Amplitude modulation (AM)—the strength or amplitude of the carrier signal is varied. This form of modulation is not often directly used in computer communication except in some modems as quadrative amplitude modulation (QAM).
(b) Frequency modulation (FM)—the frequency of the carrier is varied. This technique is often used by modems. See also frequency shift keying.
(c) Phase modulation (PM)—the phase of the carrier wave is varied. This technique is often used together with amplitude modulation in high-speed modems. See also phase shift keying.
(d) Pulse code modulation (PCM)—an analogue signal is encoded as a series of pulses in a digital data stream. This technique is used by codecs.
The process of adding a signal to an existing signal (known as the carrier) for transmission. There are two main forms of modulation used: amplitude modulation and frequency modulation. The process of recovering the signal is known as demodulation.
In general, the alteration or modification of one electronic parameter, the carrier wave, by another wave or signal, the modulating wave. The resultant composite signal is the modulated wave. The reverse process is demodulation, by which an output wave is obtained having the characteristics of the original modulating wave. If the receiver uses knowledge of the carrier’s phase to detect the modulating signals, the demodulation process is called coherent detection (or coherent demodulation); when the receiver does not utilize the carrier-phase information, the demodulation process is called noncoherent detection (or noncoherent demodulation).
The characteristics of the carrier that may be modulated are the amplitude (see amplitude modulation) or phase angle (angle modulation), particular forms being phase modulation and frequency modulation. Modulation by an undesired signal is cross modulation. Multiple modulation is a succession of processes of modulation in which the whole or part of the modulated wave from one process becomes the modulating wave for the next.
See also pulse modulation; intermodulation.
- North–South relations
- Norton’s theorem
- Norway
- Norwegian Statistical Association
- Nor’easter
- nor’wester
- NOS
- nose
- nosean
- nosecone
- no-slip boundary condition
- NoSQL
- Nostradamus (1503–66)
- no-strike agreement
- nostrils
- not
- not and
- notation
- notation, logical
- notch
- notch filter
- NOT circuit
- note
- notebook
- note frequency