A closed thermodynamic cycle used for power generation and involves raising steam from water in a boiler, expansion through a turbine, condensation, and return to the boiler (see Fig. 55). All steam turbine systems are based on adaptations of the Rankine cycle. Represented on a temperature-entropy diagram, its features include superheating, reheating, and regenerative feed heating, which are used to raise the overall cycle efficiency.
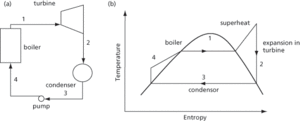
Fig. 55a and 55b
- categorial grammar
- categorical data
- categorical data analysis
- categorical/hypothetical imperative
- categorical proposition
- categorical variable
- categories
- category
- category error
- category mistake
- catena
- catenane
- catenary
- catenation
- cateniform
- catenin
- catenoid
- Cathar
- catharsis
- cathepsins
- Catherine I (1684–1727)
- Catherine II (1729–96)
- Catherine of Aragon (1485–1536)
- Catherine of Braganza (1638–1705)
- cathetometer