A large ice mass, with an area usually greater than about 50 000 km2, made up of ice domes and outlet glaciers. The Antarctic ice sheet is the world’s largest, with an area of about 13.9 × 106 km2 and a mean thickness of about 2100 m.
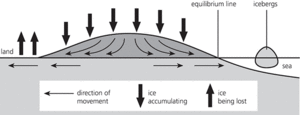
Ice sheet (cross section)
A continuous mass of glacier ice with an area over 50 000 km2; Typically an ice sheet is 1–3 km thick. Payne and Sugden (2006), ESPL 15, 7 find that both the vertical amplitude and the spatial distribution of bedrock basins and ridges are important in determining the pattern, rate, and extent of ice-sheet growth. Alley et al. (2005) Science 310, 5747 report that the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, if completely melted, could raise sea levels by about 70 m. The resulting freshwater fluxes may affect oceanic circulation. An ice core is a column of ice extracted by drilling into an ice sheet.
- browser hijacker
- browser sniffing
- Bruce, Robert
- Bruce, Sir David
- Bruce, Stanley Melbourne, Viscount Bruce of Melbourne (1883–1967)
- brucite
- Brundtland, Gro Harlem (1939)
- Brunei
- Brunel, Isambard Kingdom
- Brunhes
- Brunhilda (534–613)
- Brunner, Sir John Tomlinson (1842–1919)
- Brunner’s glands
- Bruno, Giordano
- Bruno, Giordano (1548–1600)
- ungulate
- unguligrade
- Unha rocket
- UNHCR
- uniaxial compression test
- uniaxial compressive strength
- uniaxial crystal
- uniaxial interference figure
- Unibothriocidaris
- unicarinate