The outer layer of the body of a vertebrate. It is composed of two layers, the epidermis and dermis, with a complex nervous and blood supply. The skin may bear a variety of specialized structures, including hair, scales, and feathers. This skin has an important role in protecting the body from mechanical injury, water loss, and the entry of harmful agents (e.g. disease-causing bacteria; see immunity). It is also a sense organ, containing receptors sensitive to pain, temperature, and pressure (see meissner’s corpuscles; merkel’s disc; pacinian corpuscle). In warm-blooded animals it helps regulate body temperature by means of hair, fur, or feathers and sweat glands.
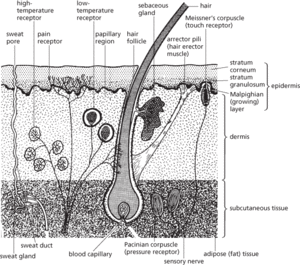
Structure of mammalian skin
- ATEX
- Athabasca
- Athanasius (c.297–373)
- Athanasius, St (c.296–373)
- atheism
- Atheismusstreit
- Athelstan (893)
- Athena rocket
- Athenian democracy
- Athenian empire
- Athens
- atherosclerosis
- Atira group
- Atiyah, Sir Michael Francis (1929–2019)
- Atkinson index
- Atkinson, Sir Harry (1831–92)
- Atkov, Oleg Yuriyevich (1949– )
- ATL
- Atlantic
- Atlantic, Battle of the
- Atlantic Charter
- Atlantic conveyor
- Atlantic Ocean
- Atlantic Period
- Atlantic Province