If the distribution of a variable is not symmetrical about the median or the mean it is said to be skewed. The distribution has positive skewness if, in some sense, the tail of high values is longer than the tail of low values, and negative skewness if the reverse is true. Skewness is quantified by the Pearson coefficient of skewness, the quartile coefficient of skewness (see quartile), or (preferably) the moment coefficient of skewness. For another measure of the shape of a distribution, see kurtosis.
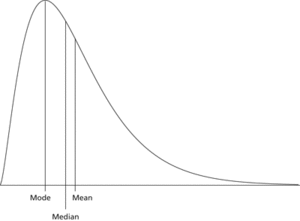
Skewed. Here it is supposed that the random variable has a finite lower bound but no upper bound. This typically results in the mean being bigger than the median and the median being bigger than the mode. The result is a positively skewed distribution.
- acquired characteristics
- acquired immune deficiency syndrome
- acquired immunity
- acquiring bank
- acquisition
- acquisition((company))
- acquisition of signal
- acquisitions approach
- acrasia
- acridine
- Acrilan
- ACRIMSAT
- acrisols
- acritarchs
- Acrobat
- acrocentric
- acrolein
- acromegaly
- acronical
- acropolis
- acrosome
- Acrothoracica
- acrozone
- Acrux
- acrylamide