An inverted U-tube with one limb longer than the other. Liquid will be transferred from a reservoir at the base of the shorter limb to the end of the longer limb, provided that the U-tube is filled with liquid. The device is useful for emptying an inaccessible container, such as a car’s petrol tank.
The pressure (p1) on the liquid at the base of the short limb (length h1) is p−h1k, where p is the atmospheric pressure and k is a constant equal to the product of the density of the liquid and the acceleration of free fall. The pressure (p2) on the liquid at the base of the long limb (length h2) is p−h2k. Thus for fluid flow to occur through the tube, from short limb to long limb, p1 > p2, and for this to occur h2 > h1. Thus if the limbs are of equal length no flow will occur; it will only occur if the limb dipping into the reservoir is shorter than the delivering limb.
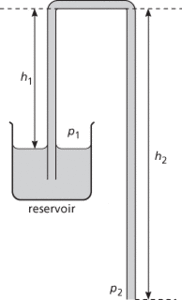
Siphon.
See syphon.
In bivalve molluscs (Bivalvia) and gastropods (Gastropoda), a tube that connects the mollusc to the world outside, funnelling water towards and away from the gills. In bivalves siphons may occur in pairs.
- optimism index
- optimization
- optimization model
- optimizer
- optimum allocation
- optimum currency area
- optimum interpolation
- optimum location
- optimum programming
- optimum reflux ratio
- optimum tariff
- opt-in email
- option
- optional product
- optional programme
- option value
- optoacoustic spectroscopy
- optoelectronics
- optoisolator
- OptSat-3000
- Opus Dei
- opx
- OQPSK
- OR
- Or