The study of the numbers of ways of selecting, or arranging, objects from a finite set. Its main applications in the theory of probability are in calculating the probability of an event such as r of the objects chosen having a particular property, or the probability of a sequence of events with a particular property. See also binomial distribution; hypergeometric distribution; negative binomial distribution.
Combinatorial results often involve factorials and binomial coefficients. For example, the probability that, in a random deal of 13 cards from a normal pack, Player A receives 13 spades is
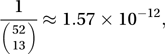 and the probability that in a random deal to four players, each player receives 13 cards of the same suit is
and the probability that in a random deal to four players, each player receives 13 cards of the same suit is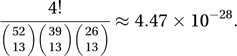
The branch of mathematics concerned with the counting problems and enumeration problems associated with such topics as combinations, permutations, number theory, arithmetic, and the theory of graphs, groups, and other discrete structures. Induction, recursion, and recurrence relations tend to play a significant role in much of this work. In computational combinatorics the underlying theory is applied to algorithms of any kind.
- UKMT
- Ukraine
- UK Space Gateway
- UKST
- ULA
- Ulam, Stanislaw Marcin
- Ulatisian
- u-law
- Ulcanian
- ULDB
- ulexite
- ullage rocket
- ulna
- Ulster
- Ulsterian
- Ulster Unionist Parties
- Ulster Volunteers
- ultimate analysis
- ultimate bearing capacity
- ultimate-cycle tuning method
- ultimate oxygen demand
- ultimate strength
- ultimate tensile strength
- ultimobranchial bodies
- ultisol