A lipid-soluble amine (see formula) that functions as both a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and a signal molecule in various roles. It is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan and occurs chiefly in enterochromaffin cells in the gut lining, in blood platelets, and in the raphe nuclei of the brainstem. In the gut, serotonin triggers responses to various mechanical or chemical stimuli, by stimulating the release of acetylcholine from neurons in the gut wall, which in turn promotes peristaltic movements of the gut musculature and secretion from glands. Serotonin also has more general effects on the activity of smooth muscles, particularly on the contraction or relaxation of blood vessel walls. Serotonergic (serotonin-releasing) neurons project from the raphe nuclei to virtually all parts of the brain and also modulate transmission in the spinal cord. Serotonin plays a key role in arousal, mood, aggression, and the sleep-wake cycle; reduced serotonin levels are associated with various disorders, including depression, migraine, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Several types of antidepressive drugs act by enhancing serotonin levels in the brain, including fluoxetine (Prozac); this is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that slows the reuptake of serotonin by neurons and prolongs its residence time in the synaptic cleft. Platelets take up serotonin from the bloodstream and release it at sites of blood clots, where it causes blood vessels to contract. Serotonin binds to a large family of serotonin (5-HT) receptors, which are coupled to diverse intracellular signal pathways. Most are metabotropic receptors, but some are coupled directly to ion channels (ionotropic). Different tissues have different types of 5-HT receptors, whereby serotonin elicits different effects. For example, serotonin binding to 5-HT2 receptors in large blood vessels causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure, whereas by binding to 5-HT1 receptors in the endings of sympathetic nerves it reduces the release of noradrenaline, which tends to reduce blood pressure. Serotonin is also found in mushrooms and in certain nuts, fruits, and vegetables. See also lysergic acid diethylamide.
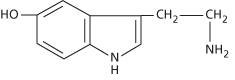
Serotonin
- probability, philosophy of
- probability space
- probability vector
- probable error
- probable error(in statistics)
- PROBA-V
- probe
- probe message
- probit
- probit analysis
- probit link
- probit model
- problematic
- problem definition
- problem description
- problem of evil
- problem of induction
- problem of other minds
- problem of points
- problem-oriented language
- problem-solving
- Proboscidea
- proboscidean
- proboscis
- procambium