A device for transferring heat from one fluid to another without permitting the two fluids to contact each other. A simple industrial heat exchanger consists of a bundle of parallel tubes, through which one fluid flows, enclosed in a container, through which the other fluid flows in the opposite direction (a counter-current heat exchanger).
A device used to transfer heat from one fluid to another without the two streams coming into contact with one another (see Fig. 23). Temperature is the driving force for heat transfer to take place in which one of the fluids is either heated or cooled. There are many types used in the chemical and process industries. Examples include condensers, kettle reboilers, evaporators, shell and tube heat exchangers, and plate heat exchangers. The choice of heat exchanger depends on the heating or cooling requirement, the thermophysical properties of the fluids, and economics.
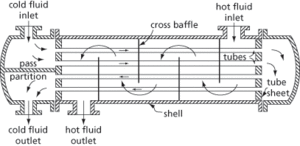
Fig. 23
- energy component
- energy dispersive spectroscopy
- energy efficiency
- energy equation
- energy flow((in ecology))
- energy gap(symbol: Eg)
- energy landscape
- energy level
- energy levels
- energy-momentum tensor
- energy of activation
- energy tax
- Engel curve
- Engelmann, George
- Engelmann, Theodor Wilhelm
- Engel process
- Engels, Friedrich (1820–95)
- Engel’s salt
- engine
- engine control unit
- engineering
- engineering data
- engineering geophysics
- engineering line diagram
- engineering model