A solid having a polygonal base with n sides, each side forming the base of a triangle. The n triangles so formed have a common vertex. The axis of the pyramid is a line joining the vertex to the centre of symmetry of the base. If the axis is perpendicular to the base the solid is a right pyramid. A square pyramid has a square base and a triangular pyramid has a triangular base (see tetrahedron). The volume of a pyramid is one third of the base area multiplied by the height.
A convex polyhedron with one face (the base) a convex polygon and all the vertices of the base joined by edges to one other vertex (the apex); thus the remaining faces are all triangular. A right-regular pyramid is one in which the base is a regular polygon and the remaining faces are isosceles triangles.
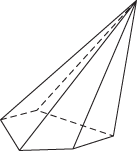
Not right-regular
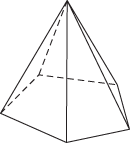
Right-regular pyramid
A crystal form composed of a number of non-parallel crystal faces which meet at a point. The crystallographic notation is frequently (111) or {111} if it is a form, whereby the crystal face intersects all the axes at their unit lengths.
A monumental structure especially characteristic of ancient Egypt, often built as a royal tomb and usually made of stone, with a square base and sloping sides meeting centrally at an apex. At first the pharaohs were buried in underground chambers over which were built rectangular mastabas; these were stone structures housing the food and accoutrements the pharaoh would need in the afterlife. Although all the interior tombs were sealed, often with elaborate devices to prevent entry, all the pyramids were robbed of their valuables in antiquity. The first pyramid was that constructed for King Zoser at Saqqara by Imhotep c.2700 bc, the so-called Step Pyramid which has six enormous steps and is over 60 m (197 feet) high. Most of the best known pyramids date from the Old Kingdom (c. 2700–2200 bc), though some were built during the eleventh and twelfth dynasties (c. 2050–1750 bc). The pyramids of Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure at Giza are a spectacular illustration of the skill of Egyptian architects – and of the state’s ability to organize a large work-force. The Great Pyramid of Giza, constructed of stone blocks of up to 200 tonnes in weight, is estimated to have required some 84,000 people employed for 80 days a year for 20 years.
Stepped pyramids known as ziggurats survive from the 3rd millennium bc in Mesopotamia. Stepped-pyramid structures were also built as bases for temples in pre-Columbian Central America. These were erected by the Mayas, Aztecs, and Toltecs, for the most part between 250 ad and 1520. The Temple of the Sun in Teotihuacán in Mexico is perhaps the most impressive.
- marguerite
- Margules’ activity coefficient model
- Margulis, Lynn
- Maria family
- marialite
- Marianas Trench
- Maria Theresa (1717–80)
- mariculture
- Marie Antoinette (1755–93)
- Marignac, Jean Charles Galissard de
- marigold
- marijuana
- marine platform
- Mariner
- Mariner Valley
- Mariotte, Edmé
- Maritain, Jacques (1882–1973)
- maritime
- maritime air
- maritime climate
- trumpet cell
- Trumpler classification
- Trumpler, Robert Julius
- truncate
- truncated cube