A test (named after Cochran and Armitage) for trend in a 2 × k contingency table where the columns correspond to categories of an ordinal variable. Denote the frequency in row i and column j by fij with i = 1 or 2, and j = 1,…, J, denote the row totals by f10 and f20, the column totals by f01,…, f0J, and the grand total by f00. The test examines the null hypothesis that, as j increases, the population proportion for a given row consistently increases (or decreases). The test statistic is T given by
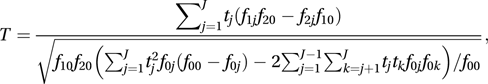 where t1, …, tk are constants chosen by the user (the optimal choice is usually tj = j, for all j). In the absence of trend, T has an approximate standard normal distribution.
where t1, …, tk are constants chosen by the user (the optimal choice is usually tj = j, for all j). In the absence of trend, T has an approximate standard normal distribution.The test is popularly used in the genetic context where J=3, the column categories are three possible genotypes labelled aa, Aa, and AA, and the rows refer to two types of individual.