If a random variable X has a probability distribution (discrete case) or a probability density function (continuous case) that can be written in the form
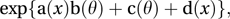 where θ is a parameter and a, b, c, and d are known functions, then it is a member of the exponential family. The Poisson distribution, the binomial distribution, and the normal distribution are members of this family. If a(x) = x, then the distribution is in canonical form and b(θ) is a natural parameter of the distribution.
where θ is a parameter and a, b, c, and d are known functions, then it is a member of the exponential family. The Poisson distribution, the binomial distribution, and the normal distribution are members of this family. If a(x) = x, then the distribution is in canonical form and b(θ) is a natural parameter of the distribution.
- Socinianism
- sociobiology
- socio-economic class
- sociology
- sociology of knowledge
- sociomedia
- socionature
- Société Française de Statistique
- sock puppet
- Socrates (469–399)
- Socratic fallacy
- Socratic irony
- Socratic method
- Socratic paradox
- SOD
- soda
- soda ash
- soda lake
- soda lime
- sodalite
- sodamide
- soda nitre
- Soddy, Frederick
- Soddy, Frederick (1877–1956)
- sodication