A statistic used to estimate the value of a population parameter. An estimator X of a parameter θ is consistent if the probability of the difference between the two exceeding an arbitrarily small fixed number tends to zero as the sample size increases indefinitely. An estimator X is an unbiased estimator of the parameter θ if E(X) = θ, and it is a biased estimator otherwise (see expected value). The best unbiased estimator is the unbiased estimator with the minimum variance. The relative efficiency of two unbiased estimators X and Y is the ratio Var(Y)/Var(X) of their variances.
Estimators may be found in different ways, including the method of maximum likelihood (see likelihood) and the method of moments (see moment).
A statistic used to estimate a parameter. The realized value of an estimator for a particular sample of data is called the estimate (or point estimate).
If the expected value of the statistic is equal to the parameter then it is described as being an unbiased estimator and the realized value is referred to as an unbiased estimate. If T is an estimator of the parameter θ and the expected value of T is θ+b, where b ≠ 0, then b is called the bias and the estimator is a biased estimator. If the bias tends to 0 as the sample size increases, then the estimator is described as being an asymptotically unbiased estimator.
The efficiency of an unbiased estimator is the ratio of its variance to the Cramér–Rao lower bound (see Fisher information). For an efficient estimator the ratio is 1. The relative efficiency of two unbiased estimators T and T ′ is given by the inverse ratio of their variances.
Comparisons involving biased estimators are often based on the mean squared error (MSE) defined to be
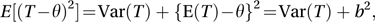 where E(T) and Var(T) are, respectively, the expected value and variance of T. The root mean square error (RMSE) is the square root of the mean squared error and has the same units as the original data.
where E(T) and Var(T) are, respectively, the expected value and variance of T. The root mean square error (RMSE) is the square root of the mean squared error and has the same units as the original data.An estimator is said to be a consistent estimator if, for all positive c,
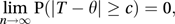 where n is the sample size.
where n is the sample size.A sufficient estimator or sufficient statistic is a statistic that encapsulates all the information provided by the data that concerns the value of the unknown parameter.
The terms ‘biased’ and ‘unbiased’ appear in an 1897 text by Bowley. The terms ‘efficiency’, ‘estimate’, ‘estimation’, and ‘sufficiency’ were introduced by Sir Ronald Fisher in 1922. The term ‘estimator’ was introduced in a specialized sense by Pitman in 1939.
A rule for using observed sample data to calculate the unobserved value of a population parameter. For example, a sample average of a variable is an estimator of the population mean of this variable. Statistical properties of an estimator, such as bias, consistency, and accuracy in a small sample, can be used to choose among various estimators typically available for the same parameter. See also estimate.
- white mica
- white muscle
- whiteness
- white noise
- white-out
- white pages
- white paper
- white peak
- white recording
- Whiterockian
- white room
- White Russians
- White Sands Test Facility
- white shark
- white spirit
- whitethroat
- White’s test
- whiting
- whitings
- Whitlam, Gough (1916–2014)
- Whitman two-film theory
- Whitney, Donald Ransom (1915–2001)
- Whitney, Eli (1765–1825)
- Whitney embedding theorem
- Whitson, Peggy (1960– )