A measure of the value of money in which the cost of a standard collection, or basket, of goods and services at some particular date is compared with the cost of the same basket at a base date. The basket is chosen to represent the expenditure of a typical household at the date under consideration.
Writing p0j and pnj as the prices at times 0 and n of the jth item in the basket, and q0j and qnj as the corresponding quantities of that item, the Laspeyres price index, suggested by Laspeyres in 1871, is the ratio
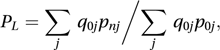 and the Paasche price index, suggested by Paasche in 1874, is the ratio
and the Paasche price index, suggested by Paasche in 1874, is the ratio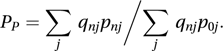 In 1922 Irving Fisher suggested using the geometric mean:
In 1922 Irving Fisher suggested using the geometric mean: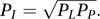 This is now known either as the Fisher index or as the ideal index. An alternative, variously known as the Bowley index, or the Marshall–Edgeworth index, is
This is now known either as the Fisher index or as the ideal index. An alternative, variously known as the Bowley index, or the Marshall–Edgeworth index, is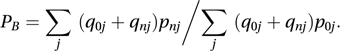 See also retail price index.
See also retail price index.
An index number, or an aggregate measure, of the prices of goods in some given category. Consider good i. Let period 0 be the base period, period t the current period, and piτ the price in period τ. The price index for good i is given by pit/pi0. This gives the index in ratio form and has a value of 1 in the base period. It is often multiplied by 100 to give a value of 100 in the base period. If a class of goods i = 1, 2,…, N is concerned, the price index is a ratio of the weighted average of their prices. The weights are the values of the goods purchased in some period. If qiτ is the quantity of good i in period τ, the base-weighted or Laspeyres price index at time t is defined as
and the current-weighted or Paasche price index at time t is defined as
Again these are in ratio form but can be multiplied by 100. Price indices can also be found for security prices or wage rates. See also consumer price index; retail price index.
- early failure period
- early humans
- early retirement
- early-type galaxy
- early-type star
- early universe
- Early voltage
- earmarking
- earned income
- earning capacity
- earnings
- earnings((company))
- earnings function
- earnings per share
- Earnshaw’s theorem
- EAROM
- ear ossicles
- earphone
- EARS
- Earth
- earth
- earth bus
- earth capacitance
- EarthCARE
- Earth Clouds, Aerosols and Radiation Explorer