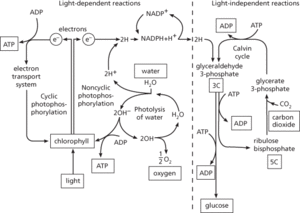
The chemical process by which green plants synthesize organic compounds from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. It occurs in the chloroplasts (most of which are in the leaves) and there are two principal types of reactions. In the light-dependent reactions, which require the presence of light, energy from sunlight is absorbed by photosynthetic pigments (chiefly the green pigment chlorophyll) and used to bring about the photolysis of water:
The electrons released by this reaction pass along a series of electron carriers (see electron transport chain); as they do so they lose their energy, which is used to convert ADP to ATP in the process of photophosphorylation. The electrons and protons produced by the photolysis of water are used to reduce NADP:
The ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions provide energy and reducing power, respectively, for the ensuing light-independent reactions (formerly called the ‘dark reaction’), which nevertheless cannot be sustained without the ATP generated by the light-dependent reactions. During these reactions carbon dioxide is reduced to carbohydrate in a metabolic pathway known as the Calvin cycle. Photosynthesis can be summarized by the equation:
Since virtually all other forms of life are directly or indirectly dependent on plants for food, photosynthesis is the basis for all life on earth. Furthermore virtually all the atmospheric oxygen has originated from oxygen released during photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis
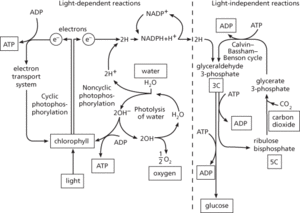
The chemical process by which green plants and other phototrophs synthesize organic compounds from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. In plants and most algae it occurs in the chloroplasts and there are two principal types of reactions. In the light-dependent reactions, which require the presence of light, energy from sunlight is absorbed by photosynthetic pigments (chiefly the green pigment chlorophyll) and used to bring about the photolysis of water:
The electrons released by this reaction pass along a series of electron carrier molecules in an electron transport chain; as they do so they lose their energy, which is used to convert ADP to ATP in the process of photophosphorylation. The electrons and protons produced by the photolysis of water are used to reduce NADP:
The ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions provide energy and reducing power, respectively, for the ensuing light-independent reactions (formerly called the ‘dark reaction’), which nevertheless cannot be sustained without the ATP generated by the light-dependent reactions. During these reactions carbon dioxide is reduced to carbohydrate in a metabolic pathway known as the Calvin–Bassham–Benson cycle. Photosynthesis can be summarized by the equation:
In photosynthetic bacteria the components of photosynthesis are arranged in folds of the plasma membrane and incorporate bacteriochlorophyll as pigment. A form of photosynthesis also occurs in archaea of the genus Halobacterium, using a membrane-bound protein called bacteriorhodopsin. Since virtually all other forms of life are directly or indirectly dependent on plants for food, photosynthesis is the basis for all life on earth. Furthermore virtually all the atmospheric oxygen has originated from oxygen released during photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis
http://www.rsc.org/Education/Teachers/Resources/cfb/photosynthesis.htm Illustrated summary of photosynthesis from the Royal Society of Chemistry
Term given to the series of metabolic reactions that occur in certain autotrophic organisms, whereby organic compounds are synthesized by the reduction of carbon dioxide using energy absorbed by chlorophyll from sunlight. In green plants, where water acts both as a hydrogen donor and as a source of released oxygen, photosynthesis may be summarized by the empirical equation:
(oxygen being released as a gas). Photosynthetic bacteria are unable to utilize water and therefore do not produce oxygen. Instead they may use hydrogen sulphide (purple and green sulphur bacteria) or organic compounds (purple non-sulphur bacteria) as a source of hydrogen.
- Satterthwaite’s formula
- saturable laser
- saturated
- saturated adiabatic lapse rate
- saturated air
- saturated compound
- saturated flow
- saturated(in networks)
- saturated mixing ratio lines
- saturated mode
- saturated model
- saturated solution
- saturated vapour pressure
- saturated velocity
- saturated zone overland flow
- saturation
- saturation current
- saturation deficit
- saturation magnetization and moment
- saturation moisture content
- saturation resistance
- saturation signal
- saturation spectroscopy
- saturation temperature
- saturation vapour pressure