A measure of the difference between two observations in a set of multivariate data.
In the case of multivariate presence/absence observations, the Hamming distance is the number of variables in which the observations differ. For example, the Hamming distance between the two binary strings 00101 and 11110 is four, since the strings differ in four positions.
By contrast, similarity is a measure of the resemblance between observations of multivariate data. Suppose two individuals are each assessed with respect to N characteristics that are either present or absent. For each characteristic there are three possible outcomes: ‘Absent for both individuals’, ‘Present for just one of the individuals’, and ‘Present for both individuals’. With the corresponding counts denoted by n0, n1, and n2, respectively, the matching coefficient is the proportion of variables in which the two classifications of the two variables agree:
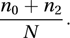 An alternative, that ignores characteristics that are absent for both individuals, is the Jaccard coefficient
An alternative, that ignores characteristics that are absent for both individuals, is the Jaccard coefficient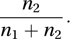 See also distance measure.
See also distance measure.
- Borel measure
- Borel set
- Borel sum
- Borel–Cantelli Lemma
- Borel–Cantelli lemma
- Borgia, Cesare (c.1476–1507)
- Borgia, Lucrezia (1480–1519)
- Borgès, Jorge Luis (1899–1986)
- boric acid
- boric anhydride
- boric oxide
- boride
- boring
- Boris Godunov (c.1551–1605)
- Borland Software Corporation
- Borlaug, Norman Ernest
- Borman, Frank (1928– )
- Bormann, Martin (1900–c.45)
- Born-Haber cycle
- bornhardt
- bornite
- Born, Max
- Born, Max (1882–1970)
- Bornu
- Born–Haber cycle