A device used to measure the flow rate of a fluid. It consists of a flat plate in which an orifice is drilled. The plate is fitted across the face of flow of a fluid in a pipe between two flanges (see Fig. 32). The shape of the orifice is usually circular and concentrically aligned with the axis of the pipe although other designs are used and may be offset to below the centreline to enable the passage of fluids carrying suspended solids. The flow of fluid through the orifice results in an increase in velocity and corresponding decrease in pressure. A measurement of the pressure drop provides a measure of the rate of flow. This type of flow meter does not allow for the recovery of energy in the fluid for which there is a high permanent energy loss. This is reflected in the coefficient of discharge of around 0.6 for high flows.
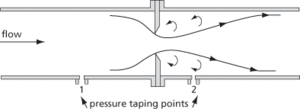
Fig. 32
- thane
- Thanetian
- Thant, U (1909–74)
- Tharsis Montes
- Thatcherism
- Thatcher, Margaret (Hilda), Baroness Thatcher of Kesteven (1925–2013)
- thaw
- TH cell
- THD
- Theaetetus (c.414–c.369)
- The Anatomy of an Internet Address
- Thebe
- theca
- the cloud
- Thecodontia
- thecodonts
- thegn
- The Great Renaming
- Theiler, Max
- The International Environmetrics Society
- theism
- thelytoky
- thema
- thematic map
- thematic mapper