An instrument used to measure the rheological properties of fluids. It consists of a cup within which fits a cylindrical bob (see Fig. 13). A sample of the fluid being tested is sandwiched between them. Either the cup is held and the bob rotated or, more rarely, the bob is held and the cup rotated. The rotational speed and distance between cup and bob define the shear rate. The torque to resist the motion defines the characteristic shear rate. The cup can be heated or cooled to determine the rheological properties as a function of temperature.
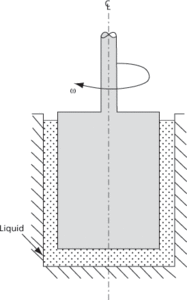
Fig. 13
- cataclasis
- cataclasite
- cataclysmic binary
- cataclysmic variable
- catacomb
- catadioptric system
- catagenesis
- Catalan numbers
- Catalan’s conjecture
- Catalan’s constant
- catalase
- Catalaunian Fields
- Catalina Sky Survey
- catalogue equinox
- catalysis
- catalyst
- catalyst poison
- catalytic activity
- catalytic coefficient
- catalytic converter
- catalytic cracking
- catalytic distillation
- catalytic hydrocracking
- catalytic reactor
- catalytic reforming