Convolution-like products occur variously in mathematics. For the Fourier transform and Laplace transform they are respectively defined by
and each is defined so that the transform of the convolution is the product of the transforms. The convolution product is commutative and the sifting property of the Dirac delta function shows it to be the identity. In probability, if f and g are the pdfs of two continuous distributions, X and Y on ℝ, then the pdf of their sum Z = X + Y is the first integral above.
A mathematical operation used in signal processing in which one set of data is smoothed (averaged) by multiplying it by another. It is often used to represent the blurring of an astronomical image due to the performance limitations of the telescope or the distorting effects of the atmosphere. See also deconvolution.
Given two independent random variables X and Y, the probability distribution of their sum, Z, is called the convolution of the distributions of X and Y. If fX (x), fY (y), and fZ (z) denote the probability density functions, then
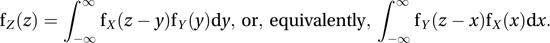 For discrete random variables the equivalent result is
For discrete random variables the equivalent result is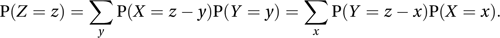
Mathematically, the operation of combining two functions, w and f, to produce a third function, g, such that
(or the corresponding continuous operation). This is envisaged as a transformation of an input function f to an output function g, by viewing f through a fixed window w.In coding theory, f is considered as a signal and w as the response of a linear channel; g is then the effect upon that signal (regarded as a sequence of successive elements) brought about by the time response of the linear channel. The channel time response is the sequence of successive elements output by the channel in response to a signal that has one element of unit amplitude and all other elements zero. The input signal sequence and the channel time response are said to be convolved.
The inverse process is deconvolution: the convolved output sequence can be deconvolved with the channel time response sequence to restore the original input signal sequence.
It is important, both mathematically and practically, that the convolution of discrete-time signals corresponds to the conventional multiplication of polynomials.
See also feedback register, feed-forward register.
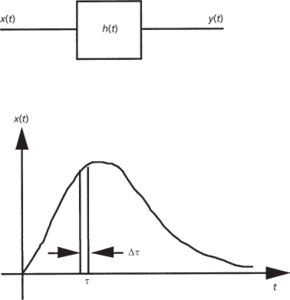
A mathematical method of analysing the response of a linear system to any input function. If an input x(t) to a linear system is split up into a succession of rectangular pulses of width Δτ so that the area of a typical pulse at t = τ is x (τ)Δτ (see diagram) then this pulse will give rise to a response
The total response y(t) can be expressed as an integral, known as the convolution integral, given by
The physical interpretation of the integral can be expressed as follows: the value of the output at a given time t is the integrated effect of the values of the input at all previous times t. This combining of two functions of the same variable is known as convolution and is expressed by the special symbol ⊗. Therefore, the general expression which defines ⊗, known as the convolution operator, is given by
Convolution
A mathematical operation (symbol *) to define the change in the shape of a wave-form caused by its passage through a filter. If an impulse response function f is convolved with an input g, then the output, h, is given by: h = g*f = ∑j × g(t − j) × f(j).