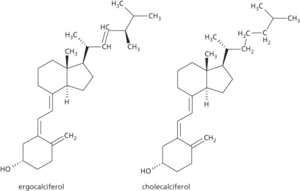
A fat-soluble vitamin occurring in the form of two steroid derivatives: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol, or calciferol), found in yeast; and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), which occurs in animals. Vitamin D2 is formed from a steroid by the action of ultraviolet light and D3 is produced by the action of sunlight on a cholesterol derivative in the skin. Fish-liver oils are the major dietary source. The active form of vitamin D is manufactured in response to the secretion of parathyroid hormone, which occurs when blood calcium levels are low. It causes increased uptake of calcium from the gut, which increases the supply of calcium for bone synthesis. Vitamin D deficiency causes rickets in growing animals and osteomalacia in mature animals. Both conditions are characterized by weak deformed bones.
Vitamin D
https://www.qmul.ac.uk/sbcs/iupac/misc/D.html Information about IUPAC nomenclature
A fat-soluble vitamin occurring in the form of two steroid derivatives: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol, or calciferol), found in yeast; and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), which occurs in animals. Vitamin D2 is formed from a steroid by the action of ultraviolet light and D3 is produced by the action of sunlight on a cholesterol derivative in the skin. Fish-liver oils are the major dietary source. The active form of vitamin D (calcitriol) is manufactured in the kidneys in response to the secretion of parathyroid hormone, which occurs when blood calcium levels are low. It causes increased uptake of calcium from the gut and promotes calcium reabsorption by the kidneys, thereby increasing the supply of calcium for bone synthesis. Vitamin D deficiency causes rickets in growing animals and softening of bones (osteomalacia) in mature animals. Both conditions are characterized by weak deformed bones.
- generalization
- generalized additive model
- generalized additive models
- generalized Church–Turing thesis
- generalized coordinates
- generalized eigenvector
- generalized estimating equations model
- generalized function
- generalized inverse
- generalized least squares
- generalized least squares (GLS) estimator
- generalized linear model
- generalized logistic equation
- generalized maximum likelihood ratio test statistic
- generalized mean value theorem
- generalized method of moments (GMM) estimator
- generalized quantifier
- generalized reciprocal method
- generalized sequential machine
- Generalized System of Preferences
- generalized uncertainty principle
- General Lifestyle Survey
- general linear group
- general linear hypothesis
- general linear model