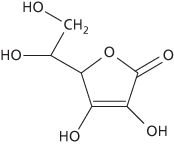
A colourless crystalline water-soluble vitamin found especially in citrus fruits and green vegetables. Most organisms synthesize it from glucose but man and other primates and various other species must obtain it from their diet. It is required for the maintenance of healthy connective tissue; deficiency leads to scurvy. Vitamin C is readily destroyed by heat and light.
Vitamin C
A colourless crystalline water-soluble vitamin found especially in citrus fruits and green vegetables. Most organisms synthesize it from glucose, but humans and other primates and various other species must obtain it from their diet. It functions as a scavenger of free radicals within cells and in extracellular fluid and blood plasma, and is needed for the synthesis of collagen, a protein found in tendons, skin, and other connective tissues. Deficiency leads to scurvy and delayed wound healing. Vitamin C is readily destroyed by heat and light.
- Weierstrass, Karl (1815–97)
- Weierstrass, Karl Wilhelm Theodor
- Weierstrass’ Approximation theorem
- Weierstrass’ theorem
- weight
- weight drop
- weighted average
- weighted code
- weighted graph
- weighted least squares
- weighted least squares estimator
- weighted mean
- weightlessness
- weights in index numbers
- Weil, André
- Weil conjectures
- Weiler–Atherton clipping algorithm
- Weil, Simone (1909–43)
- Weimar Republic (1919–33)
- Weinberg, Steven
- Weinberg, Steven (1933– )
- Weinberg–Salam model
- weir
- weird terrain
- Weismann, August Friedrich Leopold