A polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units. It is the main constituent of the cell walls of all plants, many algae, and some fungi and is responsible for providing the rigidity of the cell wall. It is an important constituent of dietary fibre. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in the textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc.
Cellulose
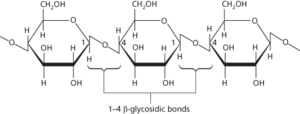
A polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units linked by 1-4 β-glycosidic bonds (see formula). It is the main constituent of the cell walls of all plants, many algae, and some fungi and is responsible for providing the rigidity of the cell wall. It is an important constituent of dietary fibre. Cellulose occurs typically as microfibrils, each consisting of long parallel arrays of 50–80 cellulose molecules. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in the textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc.
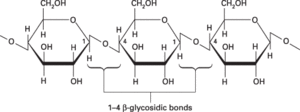
cellulose