The normal process of microbial cell division in which the paired chromosomes duplicate at the beginning of the process, and each of the daughter cells formed has pairs consisting of one original and one new and replicated chromosome. Microorganisms are used as biological catalysts in biotechnological processes such as fermentation.
A type of nuclear division that results in two daughter cells each having a nucleus containing the same number and kind of chromosomes as the mother cell. The changes during divisions are clearly visible with a light microscope. Each chromosome divides lengthwise into two chromatids, which separate and form the chromosomes of the resulting daughter nuclei. The process is divided into four stages, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, which merge into each other. Mitotic divisions ensure that all the cells of an individual are genetically identical to each other and to the original fertilized egg. See also cell cycle.
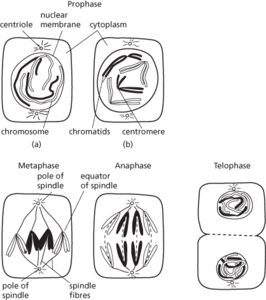
The stages of mitosis in a cell containing two pairs of homologous chromosomes
- triple root
- triplet
- triplet code
- triplex pump
- triploblastic
- triploid
- Tripolitan War (1800–15)
- tripping device
- triquetrum
- trireme
- trischiefspiegler
- trisect
- trisection of an angle
- trisector
- triserial
- trisilane
- trisodium phosphate(V)
- trisomy
- tristate logic gate
- tri-state output
- tristimulus values
- tritanopia
- tritiated compound
- tritium
- tritium clock