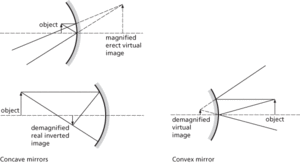
A surface that reflects most of the light falling on it. A plane mirror is a flat surface that produces an erect virtual image of a real object, in which front and back are reversed. Spherical mirrors are formed from the surfaces of spheres and form images of real objects in much the same way as lenses. A convex mirror forms erect virtual images. They are commonly used as rear-view mirrors in road vehicles, and give a diminished wide-angle image. A concave mirror can form either inverted real images or erect virtual images. Spherical mirrors obey the lens equation (using the real-positive sign convention) and are subject to some aberrations similar to those of lenses.
Mirrors.
An optical element that reflects light. A mirror may be flat (a plane mirror), which simply laterally inverts an image on reflection, or a concave or convex mirror, which forms an image. Mirrors in an optical path are always coated by aluminizing their front surface, unlike domestic mirrors which are coated on their backs. Astronomical images usually have to be very sharp, so the surface shape of the mirror must be precise. In general, the shape of an astronomical mirror should alter the reflected wavefront of light by less than a quarter of a wavelength of light across its entire surface (the Rayleigh criterion). For large mirrors, the techniques of active optics and adaptive optics are used to maintain the precise shape of the mirror. See also Segmented Mirror.
The process of keeping duplicate entities on a network. See also mirror site and data replication.
- finite resource
- finite rotation
- finite sample distribution((of a statistic))
- finite sequence
- finite series
- finite set
- finite size effects
- finite-state automaton
- finite-state machine
- finite strain
- finite‐dimensional
- finitism
- finkish
- Finland
- Finnish Statistical Society
- Finnish–Russian War (1939–40)
- fins
- Finsen, Niels Ryberg
- fiord
- FIPS
- fir
- fire
- firearm
- fire-ball
- fireball