The most efficient cycle of operations for a reversible heat engine. Published in 1824 by N. L. S. Carnot, it consists of four operations on the working substance in the engine: (1) Isothermal expansion at thermodynamic temperature T1 with heat q1 taken in. (2) Adiabatic expansion with a fall of temperature to T2. (3) Isothermal compression at temperature T2 with heat q2 given out. (4) Adiabatic compression with a rise of temperature back to T1. According to the Carnot principle, the efficiency of any reversible heat engine depends only on the temperature range through which it works, rather than the properties of the working substances. In any reversible engine, the efficiency (η) is the ratio of the work done (W) to the heat input (q1), i.e. η=W/q1. As, according to the first law of thermodynamics, W=q1−q2, it follows that η=(q1−q2)/q1. For the Kelvin temperature scale, q1/q2=T1/T2 and η=(T1−T2)/T1. For maximum efficiency T1 should be as high as possible and T2 as low as possible.
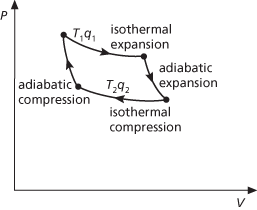
Carnot cycle.
The most efficient cycle of operations for a reversible heat engine. Published in 1824 by Nicolas Carnot, it consists of four operations on the working substance in the engine (see illustration):
a. Isothermal expansion at thermodynamic temperature T1 with heat q1 taken in.
b. Adiabatic expansion with a fall of temperature to T2.
c. Isothermal compression at temperature T2 with heat q2 given out.
d. Adiabatic compression with a rise of temperature back to T1.
According to the Carnot principle, the efficiency of any reversible heat engine depends only on the temperature range through which it works, rather than the properties of the working substances. In any reversible engine, the efficiency (η) is the ratio of the work done (W) to the heat input (q1), i.e. η = W/q1. As, according to the first law of thermodynamics, W = q1 – q2, it follows that η = (q1 – q2)/q1. For the Kelvin temperature scale, q1/q2 = T1/T2 and η = (T1 – T2)/T1. For maximum efficiency T1 should be as high as possible and T2 as low as possible.
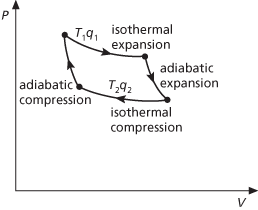
Carnot cycle
A thermodynamic cycle used in a heat engine and comprises four distinct steps: isothermal expansion, adiabatic expansion, isothermal compression, and then adiabatic compression (see Fig. 11). According to the Carnot principle, the efficiency of a heat engine depends on the temperatures at which it operates. The efficiency is the ratio of the work done, W, to the heat input, q1
where, according to the first law of thermodynamics, the work done is the difference between the heat in and heat out. The efficiency is therefore:
For maximum efficiency, T2 should be as small as possible and T1 should be as high as possible. It was developed by Nicolas Carnot in 1824.
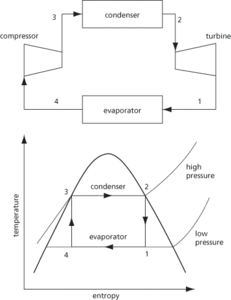
Fig. 11 Carnot steam cycle
- priority processing
- priority queue
- prior probability
- Priscoan
- Priscus, Lucius Tarquinius
- PRISM
- prism
- PRISMA
- prismane
- prismatic
- prison camps, Soviet
- prisoners’ dilemma
- prisoner’s dilemma
- Prithviraj III (died 1193)
- privacy
- privacy((mind))
- privacy((social))
- private benefit
- private branch exchange
- private chat
- private cloud
- private company
- private cost
- private enterprise
- privateers