A device for forming a magnified image of a small object. The simple microscope consists of a biconvex magnifying glass or an equivalent system of lenses, either hand-held or in a simple frame. The compound microscope uses two lenses or systems of lenses, the second magnifying the real image formed by the first. The lenses are usually mounted at the opposite ends of a tube that has mechanical controls to move it in relation to the object. An optical condenser and mirror, often with a separate light source, provide illumination of the object. The widely used binocular microscope consists of two separate instruments fastened together so that one eye looks through one while the other eye looks through the other. This gives stereoscopic vision and reduces eye strain. See also atomic force microscopy; electron microscope; field-emission microscope; field-ionization microscope; phase-contrast microscope; scanning tunnelling microscopy; ultraviolet microscope. See also Microscopy (Chronology).
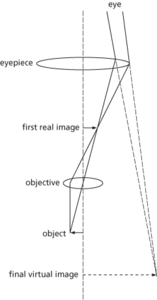
Microscope. Compound microscope.
Any device for forming a magnified image of a small object. The simple microscope consists of a biconvex magnifying glass or an equivalent system of lenses, either hand-held or in a simple frame. The compound microscope uses two lenses or systems of lenses, the second magnifying the real image formed by the first (see illustration). The lenses are usually mounted at the opposite ends of a tube that has mechanical controls to move it in relation to the object. An optical condenser and mirror, often with a separate light source, provide illumination of the object. The widely used binocular microscope consists of two separate instruments fastened together so that one eye looks through one while the other eye looks through the other. This gives stereoscopic vision. See Chronology. See also confocal fluorescence microscopy; electron microscope; nomarski microscope; phase-contrast microscope; scanning probe microscopy; ultraviolet microscope.
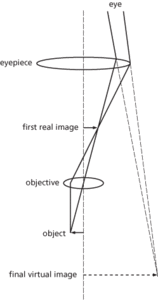
Compound microscope
http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/index.html Accessible and entertaining portal from Microscopy UK
- electronic bill presentment and payment
- electronic blackboard
- electronic book
- electronic brakeforce distribution
- electronic brokerage
- electronic business
- electronic cheque
- electronic commerce
- electronic commerce agent
- electronic data interchange
- electronic data processing
- electronic device
- electronic discovery
- electronic effects
- electronic efficiency
- electronic filing
- Electronic Frontier Foundation
- electronic funds transfer at point of sale
- electronic funds transfer system
- electronic goods
- electronic graffiti
- electronic image stabilization
- electronic imaging
- electronic ink
- electronic journal